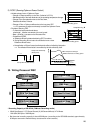
30
3) Recording format using phase-change recording material (DVD-RW/DVD+RW)
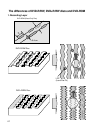
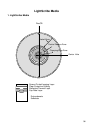
* Data is recorded by changing the recording layer from the amorphous status to the crystalline status, and
played back by reading the difference of the reflection coefficient.
[ Amorphous : Non-crystalline ]
Substrate
Laser beam
Recording data
(Melting/Quick cooling)
Erasing data
(Heating/Gradual cooling)
Data erased state
(High reflection coefficient)
Recorded state
(Low reflection coefficient)
Crystalline status
Amorphous status
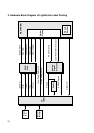
DVD-RW
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Dielectric layer
Recording layer
(Phase change material)
Dielectric layer
Disc substrate
DVD+RW
Adhesive layer
Protective layer
Reflective layer
Dielectric layer
Recording layer
(Phase change material)
Dielectric layer
Disc substrate
> Disc structure
> Recording principles
[Recording]
When a high-power laser is applied to the recording material, it melts and then becomes amorphous with
a low reflection coefficient when it quickly cools off. When a mid-power laser is applied to heat gradually
the recording material and then gradually cools it off, it becomes crystal with a high reflection coefficient.
[Playback]
A low-power laser is used for playback. The amount of reflected light depends on the status (amorphous
or crystalline) of the recording material. This is detected by an optical sensor.