6 F 3 B 0 3 6 4
29
1.4.2 The Bit Strobe Instruction/Response Mode
The bit strobe instruction/response mode is used for exchanging a small size of data between the
master device ⇔ slave devices. In the bit strobe instruction, based on the information obtained
from the scan list, the master device broadcasts 1-bit output data to individual slave devices.
These individual devices transmit data (0
-
8 bytes) in response to the bit strobe instruction to the
master device (bit strobe response).
It depends on the specification of a slave device how the salve device interprets a bit strobe
instruction and what data the slave device transmits to the bit strobe response.
For this communication function, it is prerequisite that the slave device supports the bit strobe
instruction/response mode.
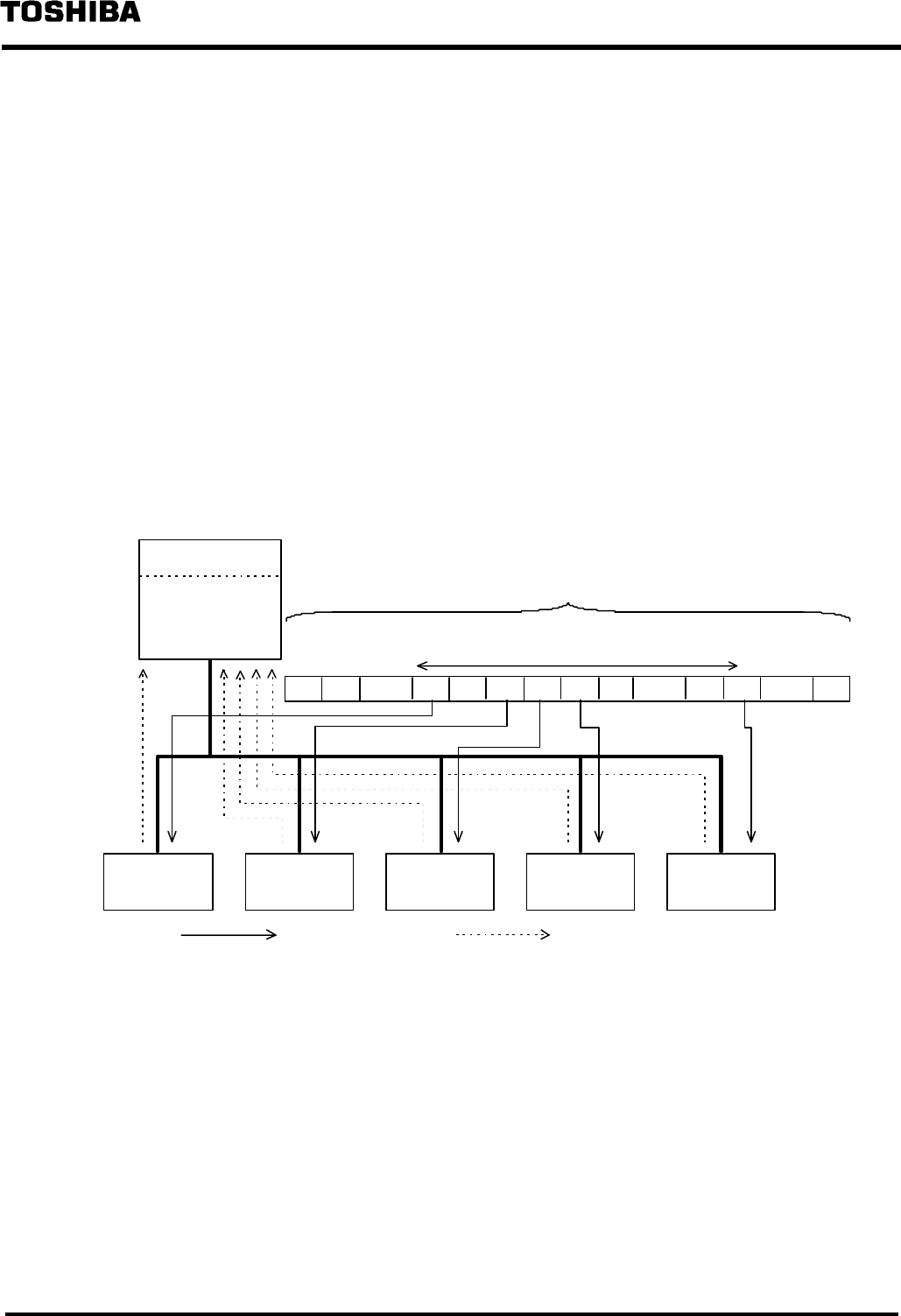
(1) The Bit Strobe Instruction
Broadcasts data to bit strobe instruction/response mode supporting slave devices on the network.
The bit strobe instruction contains 64
-
bit output data, and each of the 64 bits is assigned to
individual node addresses on the network (Figure 1. 9).
The example in Figure 1.9 indicates the DN211 is inputting sensor information by the bit strobe
mode and trying to send output control data to the actuator. The way of writing output data in bit
strobe from the T2/T2E/T2N to the DN211 is explained in "5. Communication with Salve Devices."
Slave 4
Photoelectric
sensor
NA = 23
Slave 3
Photoelectric
sensor
NA = 22
Slave 5
Actuator
NA = 52
Slave 2
Proximity sensor
NA = 21
Slave 1
Proximity sensor
NA = 19
T2/T2E/T2N
Master
DN211
NA = 1
Bit strobe responseBit strobe instruction /
Bit number
Bit strobe instruction data
• • • •• • • •• • • •
6351 5219 20 21 22 23 240 1
Figure 1.9 Example of the Bit Strobe Instruction/Response Mode
(2) The Bit Strobe Response
A slave device which received the bit strobe instruction transmits 0 to 8 byte response data to the
master device. The contents of response data varies depending on the specification of the slave
device. The way the T2/T2E/T2N reads bit-strobe response data from the DN211 is described in
"5. Communication with Slave Devices."