TP Receivers • Installation and Operation
TP Receivers • Installation and Operation
Installation and Operation, cont’d
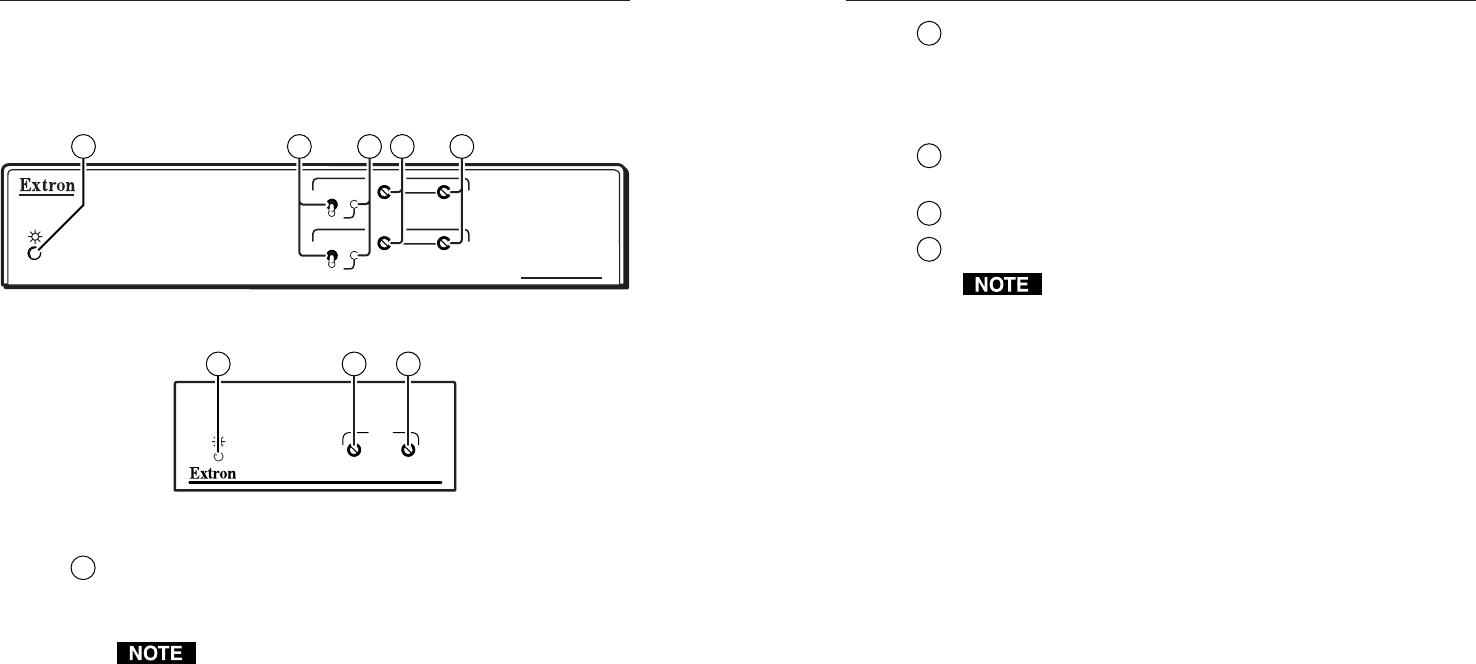
Front Panel Controls and Indicators
The TP R BNC A and TP R BNC AV have similar controls and
indicators (figure 2-12). The TP R 15HD A has a reduced set of
controls (figure 2-13).
TP R BNC AV
VIDEO
MANUAL
AUTO
LEVEL PEAKING
RGB
MANUAL
AUTO
LEVEL PEAKING
1
2 3 4 5
Figure 2-12 — TP R BNC AV control and indicators
TP R 15HD A
RGB
PEAKING
LEVEL
1
4 5
Figure 2-13 — TP R 15HD A control and indicators
1
Power LED
Amber — indicates that power is applied, but that the
transmitter is not connected to a receiver.
On the TP R BNC AV only, and only if the composite
video TP link is used and the RGB link is not used, this
LED will only light amber.
Green — indicates that a transmitter is connected and any
of the following grounding conditions exist:
• The transmitter is powered by a local power supply
and the receiver’s output is connected to a device
that provides a reference ground.
• The transmitter is powered by the receiver, is locally
grounded, and the receiver’s output is connected to
a device that provides a reference ground.
• The transmitter is receiving power from the
receiver, a local monitor is connected to the
transmitter, and the receiver’s output is connected
to a device that provides a reference ground.
• The receiver is connected to a TP switcher that is
connected to a device that provides a reference
ground.
2
Manual/Auto switch (TP R BNC A and TP R BNC AV) — With
this switch in the Auto position, the receiver automatically
adjusts the level and peaking to compensate for long cable runs.
In the Manual position, you can manually compensate for long
cable runs using the level and peaking controls.
3
Auto LED (TP R BNC A and TP R BNC AV) — Indicates that
the Manual/Auto switch is in the Auto position.
4
Level control — Adjusts the image brightness.
5
Peaking control — Adjusts the image sharpness.
For details on the SOG and C SYNC switches, see
Computer video earlier in this chapter.
Troubleshooting
If the image does not appear
1. Ensure that all devices are receiving power. The
transmitter’s and receiver’s front panel Power LEDs
indicate that they are receiving power.
2. Ensure that the transmitter is receiving a video input.
3. Ensure that the TP cable(s) are properly terminated in
accordance with TIA/EIA T 568A standards and that the
RJ-45 connections are securely made. If the Power LEDs
on the transmitter and the receiver are lit green, a
transmitter is properly connected to a receiver.
4. For computer/RGB video, ensure that the receiver’s SOG
and C Sync switches are in the correct positions for the
video output.
5. For computer video, ensure that the transmitter’s ID bit
switches are on.
6. For computer video on an LCD projector, ensure that the
transmitter’s DDSP switch is on.
7. The transmission distance may be too far for remote
power. Try connecting the local 15V power supply to the
transmitter.
8. The transmission distance may be too short. Ensure that
the UTP cable is at least 50 feet long.
9. If the Manual/Auto switch is in the manual position,
ensure that the receiver’s level controls are not set too
high. Too much level and peaking can cause display
problems.
2-18 2-19