22
3) CD-RW Disc
4.
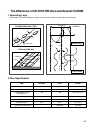
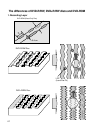
Reading process of Optical Disc
Laser Beam
Groove
Substrate
(Polycarbonate)
Recording Layer
Dielectric Layer(TL)
Dielectric Layer(UL)
Protective Layer
Label Printing
• It is composed of polycarbonate layer, alloy(silver, arsenic) layer, aluminum reflectivity layer, protective layer.
• An crystalized alloy layer is transformed into noncrystalized by the laser heat. Therefore, writing and reading
is enabled by the difference of reflectivity.
• It is possible to overwrite about 1000 times.
• Laser Wavelength : 780 nm, Laser Power (Read) : 1.0mW
• Recording Power : Erase (4~18mW), Write (6~45mW)
• When disc rewriting, new data is overwritten previously recorded data.
• Polycarbonate layer has a Pre-Groove which make a track.
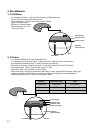
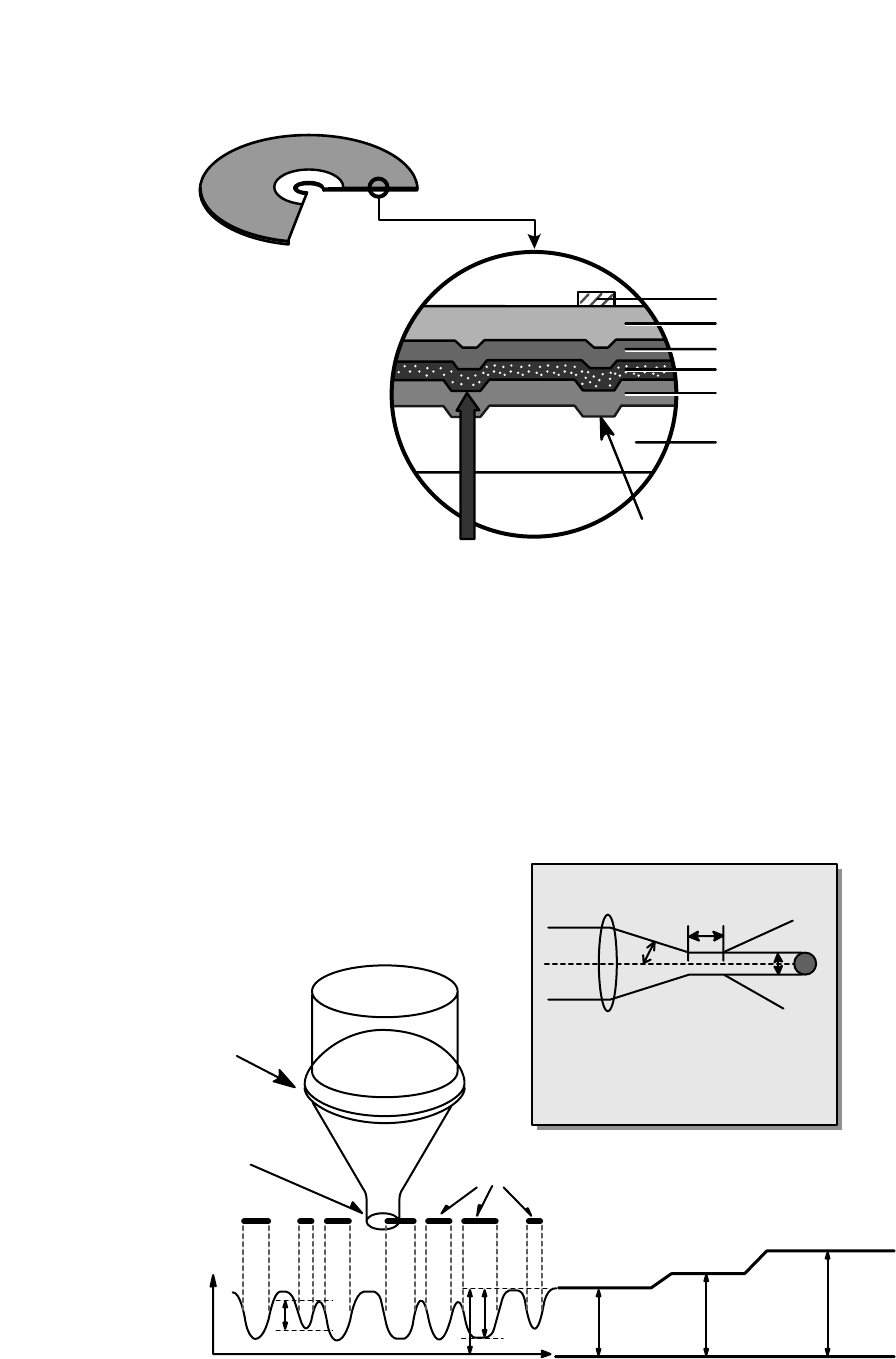
Lens
H
D
Beam
Spot
Focusing
Lens
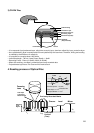
Laser Spot
at Constant
Read Intensity
Reflected
Light
Signal
Laser Spot
Position
(Time)
Previously Recorded Marks
Groove Land Mirror
I
3
I
top
I
11
I
G
I
L
I
0
Numerical aperture: NA=nsin
θ
,
n: Refractive index
Focus depth : H =
λ
/NA
laser spot diameter : D =
λ
/NA
2
θ