15
Tips
Glossary
Poor reception The proximity of mountains or high buildings may be responsible for ghost pictures,
echoing or shadows. In this case, try manually adjusting your picture: see Finetune (p.7)
or modify the orientation of the outside aerial. If you are using an indoor aerial, recep-
tion may be difficult in certain conditions. You can improve reception by rotating the
aerial. If the reception remains poor, you will need to use an external aerial.
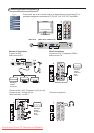
No picture Have you connected the aerial socket properly ? Have you chosen the right system? (p.7).
Poorly connected euroconnector cables or aerial sockets are often the cause of picture
or sound problems (sometimes the connectors can become half disconnected if the TV
set is moved or turned). Check all connections.
No sound If on certain channels you receive a picture but no sound, this means that you do not
have the correct TV system. Modify the System setting (p.7). The amplifier connected to
the TV does not deliver any sound? Check that you have not confused the audio output
with the audio input.
How to switch
TV / PC mode ?
Press AV key on remote control and select PC mode in Source List. (p.12)
First of all, you must connect your computer to VGA jack on the back of TV and adjust
to best resolution.
For laptop user, please press “Fn
” + “CRT/LCD” buttons to switch the screen to TV.
PC mode don’t
work ?
Check that you have configured the computer on a compatible display
resolution (see p.12).
Remote control The TV set does not react to the remote control; the indicator on the set no longer
flashes when you use the remote control? Replace the battery.
Standby If the set receives no signal for 30 mins, it automatically goes into standby mode. To save
power, your set is fitted with components that give it a very low power consumption
when in standby mode (less than 1 W).
Cleaning the set Only use a clean, soft and lint-free cloth to clean the screen and the casing of your set.
Do not use alcohol-based or solvent-based products.
Still no results? Disconnect the mains plug of the TV for 30 seconds then reconnect it. If your TV set
breaks down, never attempt to repair it yourself: contact your dealer’s after-sales
service.
VGA (Video Graphics Array): a common stan-
dard graphics display system for PCs.
RGB signals : These are the three video signals,
Red Green Blue, which make up the picture.
Using these signals improves picture quality.
S-VHS Signals: These are 2 separate Y/C video
signals from the S-VHS and Hi-8 recording stan
-
dards.The luminance signals Y (black andwhite)
and chrominance signals C (colour) are recorded
separately on the tape.This provides better
picture quality than with standard video(VHS and
8 mm) where the Y/C signals are combined to
provide only one video signal.
NICAM sound: Process by which digital sound can
be transmitted.
System: Television pictures are not broadcast in
the same way in all countries. There are different
standards: BG, DK, I, and L L’. The System setting
(p.7) is used to select these different standards. This
is not to be confused with PAL or SECAM colour
coding. Pal is used in most countries in Europe,
Secam in France, Russia and most African countries.
The United States and Japan use a different system
called NTSC. The input EXT is used to read NTSC
coded recordings.
16:9: Refers to the ration between the length and
height of the screen. Wide screen televisions have
a ration of 16/9, conventional screen TV sets have a
ration of 4/3.
Downloaded From TV-Manual.com Manuals