CONFIDENTIAL – DO NOT COPY
Page 8-45
File No. SG-0184
Operations :
Reads
Subsequent to programming the mode register with CAS latency, burst type, and burst length,
Read bursts are initiated with a Read command.
The starting column and bank addresses are provided with the Read command and Auto
Precharge is either enabled or disabled for that burst access. If Auto Precharge is enabled, the
row that is accessed starts precharge at the completion of the burst, provided tRAS has been
satisfied. For the generic Read commands used in the following illustrations, Auto Precharge is
disabled.
During Read bursts, the valid data-out element from the starting column address is available
following the CAS latency after the Read command. Each subsequent data-out element is valid
nominally at the next positive or negative clock edge (i.e. at the next crossing of CK and CK). The
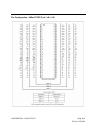
following timing figure entitled “Read Burst: CAS Latencies (Burst Length=4)” illustrates the
general timing for each supported CAS latency setting. DQS is driven by the DDR SDRAM along
with output data. The initial low state on DQS is known as the read preamble; the low state
coincident with the last data-out element is known as the read postamble . Upon completion of a
burst, assuming no other commands have been initiated, the DQs and DQS goes High-Z. Data
from any Read burst may be concatenated with or truncated with data from a subsequent Read
command. In either case, a continuous flow of data can be maintained. The first data element
from the new burst follows either the last element of a completed burst or the last desired data
element of a longer burst which is being truncated. The new Read command should be issued x
cycles after the first Read command, where x equals the number of desired data element pairs
(pairs are required by the 2n prefetch architecture). This is shown in timing figure entitled
“Consecutive Read Bursts: CAS Latencies (Burst Length =4 or 8)”.A Read command can be
initiated on any positive clock cycle following a previous Read command. Nonconsecutive Read
data is shown in timing figure entitled “Non-Consecutive Read Bursts: CAS Latencies (Burst
Length = 4)”. Full-speed Random Read Accesses: CAS Latencies (Burst Length = 2, 4 or 8)
within a page (or pages) can be performed as shown on following: