24
(b) Effects to relay life due to connected load
The actual relay life may be significantly shortened compared to the relay life curve, depending on the type of a
load connected and the characteristics of inrush current. ( Page 23, Section 3.2 (3) (a)) Also, the inrush
current may cause the module contact welding.
Take the following measures to prevent shortening of the relay life and the contact welding.
• Select a load so that the inrush current will be within the rated current of the module.
• Connect an external relay that can withstand the inrush current.
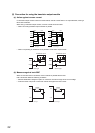
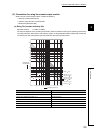
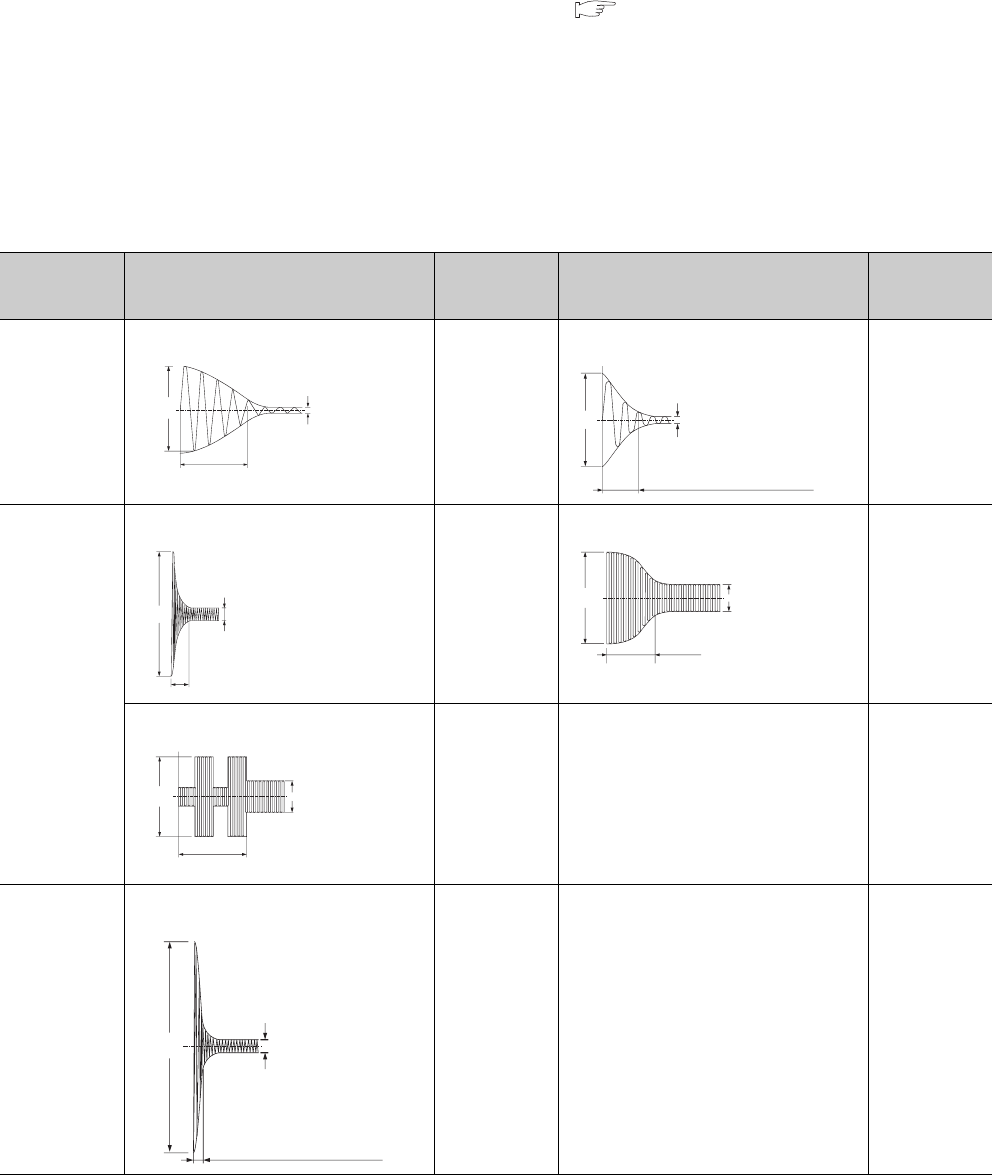
The following table shows the relation between the road and the inrush current.
Select a load so that the inrush current (i) and the rated current (io) will be within the rated switching current
specified for the output module used.
The inrush current may flow for a longer time depending on the load.
*1 Typical electric-discharge lamp circuit includes discharge tubes, transformers, choke coils, and capacitors. Therefore,
note that the inrush current may flow 20 to 40 times as large as the rated current in the case of high power factor and low
power impedance.
*2 When the wiring of the circuit is long, take care of the wire capacity.
Load type Signal waveform diagram
Inrush current
(i)/rated current
(io)
Signal waveform diagram
Inrush current
(i)/rated current
(io)
Inductive load
Approx. 10 to 20
times
Approx. 3 to 10
times
Lamp load
Approx. 3 to 10
times
Approx. 3 times
*1
Approx. 5 to 10
times
Capacitive load
Approx. 20 to 40
times
i
i
o
0.07 to 0.1 seconds
Load of a solenoid
i: Inrush current
i
o: Rated current
0.017 to 0.033 seconds
(1 to 2 cycles)
i
i
o
i: Inrush current
i
o
: Rated current
Load of an electromagnetic contactor
i: Inrush current
i
o
: Rated current
i
o
Load of an incandescent bulb
i
Approx. 0.33 seconds
Load of a mercury lamp
i
i
o
180 to 300 seconds
(3 to 5 minutes)
i: Inrush current
i
o: Rated current
i: Inrush current
i
o: Rated current
Load of a fluorescent
i
o
Within 10 seconds
i
0.008 to 0.33 seconds
(0.5 to 2 cycles)
Capacitive load
*
2
i: Inrush current
i
o
: Rated current
i
o
i