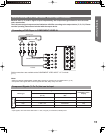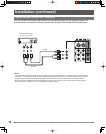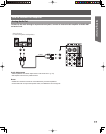
23
Getting Start ed
RGB signals that can be input
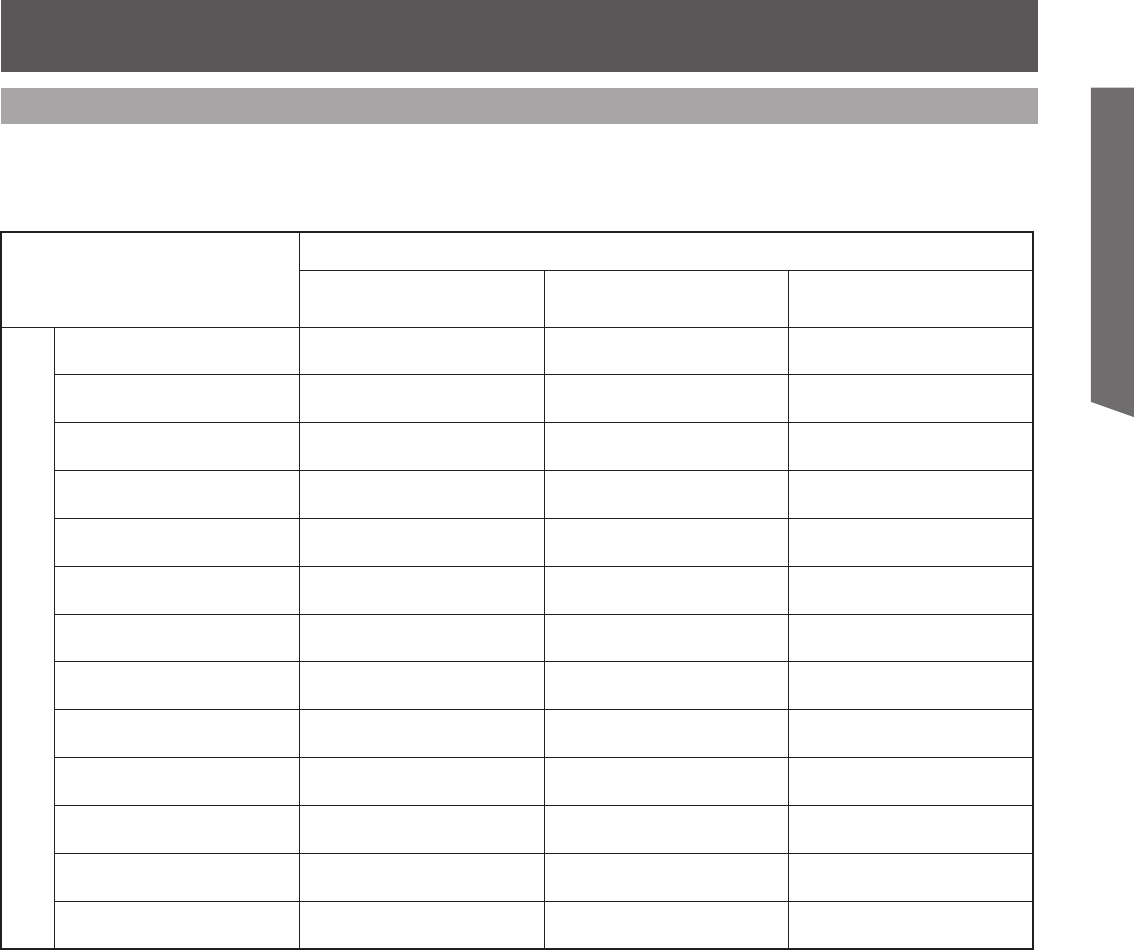
The table below lists the different types of RGB signals that can be input.
If a signal which differs greatly from the types listed below is input, the picture may not be displayed
correctly, or a black background may be displayed.
Notes:
• Input signals, other than those listed with a * mark, will give you a beautiful, stable picture.
• The D-SUB 15P connector can accept RGB (H-V sync separate).
• When an external video processor/scaler is used, it must have RGB (H-V sync separate) output.
Mode type
Signal data
No. of dots
(H × V)
Horizontal frequency
(kHz)
Vertical frequency
(Hz)
Personal Computer Signals
VGA400 (70 Hz) 640 × 400 31.47 70.08
VGA480 (60 Hz) 640 × 480 31.47 59.94
Macintosh 13˝ 640 × 480 35.00 66.67
VGA480 (75 Hz) 640 × 480 37.50 75.00
SVGA (60 Hz) 800 × 600 37.88 60.32
SVGA (75 Hz) 800 × 600 46.88 75.00
SVGA (85 Hz) 800 × 600 53.67 85.06
Macintosh 16˝ 832 × 624 49.73 74.55
* XGA (60 Hz) 1 024 × 768 48.36 60.00
* XGA (70 Hz) 1 024 × 768 56.48 70.07
* XGA (75 Hz) 1 024 × 768 60.02 75.03
* XGA (85 Hz) 1 024 × 768 68.67 85.00
* Macintosh 21˝ 1 152 × 870 68.68 75.06