Chapter 2 System Features 2-5
2.1.2 Memory Subsystem
The memory subsystem controls memory access and cache memory. The
M8000/M9000 servers use DDR-II DIMM memory.
Each CMU has thirty-two memory slots.
Also, the M8000 server, M9000 server, and M9000 server with expansion cabinet can
mount up to 128, 256, or 512 DIMMs, respectively.
The memory subsystems use up to eight-way interleaving, providing higher-speed
memory access.
Memory mirror mode is supported for every pair of memory buses in a CMU. This
enables continued operation using the other non-defective bus if an error occurs in
one bus. Memory mirror mode can be set up by the system administrator.
2.1.3 I/O Subsystem
The I/O subsystem controls data transfer between the main unit and I/O devices.
The M8000/M9000 servers use PCIe as the interconnect bus for I/O devices.
Each IOU contains eight-lane (x8) PCIe slots. Also, eight-lane PCIe slots or 133-MHz
64-bit PCI-X slots can be in a mounted through an External I/O Expansion Unit.
The M8000 server, M9000 server, and the M9000 server with expansion cabinet can
mount up to 32, 64, or 128 PCIe-compatible cards, respectively.
PCI Express slots or PCI-X slots can be added by mounting an External I/O
Expansion Unit through a PCI Express slot.
2.1.4 System Bus
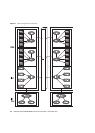
The CMU containing a CPU and memory subsystem and each component in an IOU
containing an I/O subsystem are used for high-throughput data transfer between all
components through a crossbar switch. The crossbar switch has duplicated bus
routes. If one crossbar switch has an error, the system can be restarted to isolate the
faulty switch, enabling the high-end servers to continue operation.
FIGURE 2-2 shows data transfer in the system.