3-2 SPARC Enterprise M8000/M9000 Servers Overview Guide • December 2010
3.1.1 Domain Management
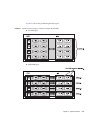
In the M8000/M9000 servers, a physical system board (PSB) can be logically divided
into one part (no division) or four parts by a partitioning function unique to the
system.
A PSB that is logically divided into one part (no division) is called a Uni-XSB, and a
PSB that is logically divided into four parts is called a Quad-XSB.
The physical unit configuration of each divided part of a PSB is called an extended
system board (XSB).
In the M8000/M9000 servers, a domain can be configured with any combination of
these XSBs.
3.1.2 PCI Hot-plug
M8000/M9000 servers support insertion and removal of PCI cards for specific PCI
Express and PCI-X hot-plug controllers. Before removing the PCI card, be sure to
cancel the settings and isolate the card by using the Oracle Solaris OS cfgadm(1M)
command, and make sure that the card is physically removable.
For details of PCI hot-plug, see the SPARC Enterprise
M3000/M4000/M5000/M8000/M9000 Servers Administration Guide.
3.2 XSCF Firmware Function
The XSCF firmware is a System Control Facility including a dedicated processor that
is independent from the processors in the server. This section describes XSCF
firmware features and provides an overview of XSCF firmware functions.
3.2.1 XSCF Features
The XSCF is firmware that is preinstalled, and operates on the XSCFU as standard
equipment. As long as input power is being supplied to the server, the XSCF
constantly monitors and manages the server even if the power to domains is turned
off. In addition, the XSCF provides a user interface from which users can operate
and manage the server.