2-10 SPARC Enterprise M8000/M9000 Servers Overview Guide • December 2010
2.2.3 Domain Configuration
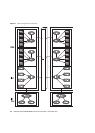
Any XSBs in the server can be combined to configure a domain, regardless of
whether the divided XSB is the Uni-XSBs or Quad-XSBs.
These XSBs can be used in any combination for a flexible domain configuration.
Also, the quantity of resources for one XSB can be adjusted according to the division
type of a PSB. Thus, a domain can be configured based on the quantity of resources
required for job operations.
XSCF user interfaces are used to configure a domain. Each configured domain is
managed by the XSCF.
The maximum number of domains that can be configured in the servers depends on
the system. Up to 16 domains can be configured in M8000 servers, and up to 24
domains can be configured in M9000 servers.
To configure a domain, an LSB number must first be assigned so that a logical
system board (LSB) can function as an LSB of the XSB.
This LSB number is referenced by the Oracle Solaris OS, and it must be a unique
number in the domain. However, if one XSB is shared by multiple domains, a
common LSB number need not be defined in the domains. An arbitrary LSB number
can be assigned for this setting in each domain.
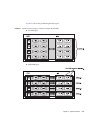
Domain configuration settings are made for each domain. A domain can be
configured by specifying an XSB together with this LSB number.
Up to 16 XSBs can be configured in a single domain.
The following as well as the quantity of resources must be considered by the user
who is specifying the domain configuration and division type:
■ The Uni-XSB type is suitable in the configuration of a domain requiring a large
quantity of resources. Also, an XSB of the Uni-XSB type is separated by the
physical configuration units of a CMU and IOU. Thus, if a hardware error occurs
in a CPU or memory, hardware can easily be replaced without affecting other
domains. However, a resource quantity decrease due to an error may be in the
range specified by the PSB.
■ Quad-XSB type is suitable in the configuration of a small-scale domain, and
optimized for flexible resource management. However, since domains are
logically separated in a PSB, an error in the hardware shared within the PSB may
affect other domains.
In addition, resources of a configured domain can be added to and deleted from
individual XSBs, and they can be moved between domains by using DR function.