7
Used with its optional copy protection scheme, DVI
makes it possible to view full resolution signals with-
out exposing the signal to copyright infringement.
It is the digital equivalent of component DTV con-
nections (Y,Pr,Pb) that can be configured for use in
a copy protected environment.
The DVI standard supports the following…
• Analog only interface (DVI-A)
• Digital only interface (DVI-D)
• Analog or Digital interface (DVI-I)
• Transition Minimized Differential Signaling
(TMDS)
• Display Data Channel (DDC)
• Extended Display Identification Data
(EDID)
• High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection
(HDCP)
• Hot Plug Detect (HPD)
• Digital Monitor Power Management
(DMPM)
A glossary of acronyms is provided in Table 5.
DVI-A, DVI-D, DVI-I
DVI can provide an analog link, DVI-A, or a digital
link, DVI-D. The integrated link, DVI-I, was de-
signed to support either. Each link has its own type
connector, covered later in this article. MonitorLink
uses digital only DVI, so the focus of the remainder
of this discussion will concentrate on the digital link.
DDC Display Data Channel
DDWG Digital Display Working Group
DMPM Digital Monitor Power Management
DVI-A Digital Visual Interface - Analog
DVI-D Digital Visual Interface - Digital
DVI-I Digital Visual Interface - Integrated (Digital or Analog)
EDID Extended Display Identification Data
HDCP High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection
TMDS Transistion Minimized Differential Signaling
VESA Video Electronics Standards Association
Acronyms
Table 5
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling
(TMDS)
TMDS is a method used to transmit digital data that
reduces the number of bit transitions (high to low or
low to high) occurring in the serial bit stream. To
reduce the transitions, it uses an advanced formula
(algorithm) that converts 8 bit data into 10 bit data.
Differential circuitry is then used to output compli-
mentary signals. The results are…
• Reduced Electromagnetic Interference
(EMI).
• Faster transfer rates with reduced errors.
• Ability to use twisted pair wire vs. coax.
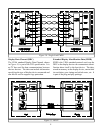
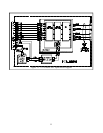
A TMDS link consists of a TMDS Transmitter that
encodes and sends a data stream to a TMDS Receiver,
see Figure 10. Three sets of twisted pair wires carry
the Red, Green and Blue data. An additional twisted
pair carries the timing clock signal.
Because the bandwidth over copper wire is limited
to about 165 MHz, DVI can use up to two TMDS
links, or 6 channels sharing the same clock. DVI
with a dual-link TMDS has a bandwidth that is
doubled.
1080i HDTV, with a pixel rate of 1920 X 1080 at
30Hz can be supported by a DVI interface operating
in the single-link mode.