HYUNDAI MicroElectronics GMS90X5XC Series
22 Jan. 2001 Ver 1.0
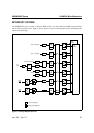
A low-priority interrupt can itself be interrupted by a high-priority interrupt, but not by another low priority in-
terrupt. A high-priority interrupt cannot be interrupted by any other interrupt source.
If two requests of different priority level are received simultaneously, the request of higher priority is serviced.
If requests of the same priority are received simultaneously, an internal polling sequence determines which re-
quest is serviced. Thus within each priority level there is a second priority structure determined by the polling
sequence as shown in Table 9.
Table 8. Interrupt Sources and their Corresponding Interrupt Vectors
Source (Request Flags) Vectors Vector Address
RESET
IE0
TF0
IE1
TF1
RI
+
TI
TF2
+
EXF2
RESET
External interrupt 0
Timer 0 interrupt
External interrupt 1
Timer 1 interrupt
Serial port interrupt
Timer 2 interrupt
0000H
0003H
000BH
0013H
001BH
0023H
002BH
Table 9. Interrupt Priority-Within-Level
Interrupt Source Priority
External Interrupt 0
Timer 0 Interrupt
External Interrupt 1
Timer 1 Interrupt
Serial Channel
Timer 2 Interrupt
IE0
TF0
IE1
TF1
RI + TI
TF2 + EXF2
High
↓
↓
↓
↓
Low