3 - 10 3 - 10
MELSEC-Q
3 SPECIFICATIONS
3.2 Function List
Table 3.2 shows the function list of the A/D converter modules.
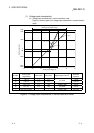
Table 3.2 Function list
Item Function Reference section
A/D conversion enable/
disable setting
(1) Specifies whether to enable or disable the A/D conversion for each channel.
(2) By disabling the conversion for the channels that are not used, the
sampling time can be shortened.
Section 3.4.2
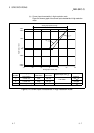
A/D conversion method
(1) Sampling processing
The A/D conversion for analog input values is performed successively for
each channel, and the digital output value is output upon each conversion.
(2) Averaging processing
For each channel, A/D conversion values are averaged for the set number of
times or set amount of time, and the average value is output as a digital value.
Section 3.2.1
Maximum and minimum
values hold function
(1) The maximum and minimum values of the digital output values is retained
in the module.
Section 3.2.2
Temperature drift
compensation function
(1) Errors arising from changes in the ambient temperature of the module are
automatically compensated for to improve conversion accuracy.
(2) The temperature drift compensation function can be performed at (A/D
conversion time for all channels) + 160
s.
——
Resolution mode
(1) The resolution mode can be switched according to the application, and digital-
value resolution settings of 1/4000, 1/12000 or 1/16000 can be selected.
(2) The resolution mode setting is applicable to all channels.
(3) See Section 3.1.1 for the digital output values and maximum resolution in
normal resolution mode and high resolution mode.
Section 3.1.1
Section 4.5
Online module change (1) A module change is made without the system being stopped. Chapter 7
3.2.1 A/D conversion methods
There are two A/D conversion methods, sampling processing and averaging processing.
(1) Sampling processing
A/D conversion is performed successively for the analog input value, and the
converted digital output values are stored in the buffer memory.
The sampling processing time depends on the number of channels used (the
number of channels set to A/D conversion enable) and whether the temperature
drift compensation function is available.
(a) Without the temperature drift compensation function
(Processing time) = (Number of channels used)
80 ( s/1 channel)
(b) With the temperature drift compensation function
(Processing time) = (Number of channels used)
80 ( s/1 channel) + 160 s
[Example]
When three channels (channels 1, 2 and 4) are A/D conversion enabled with the
temperature drift compensation function, the sampling processing time is 400
s.
3
80 + 160 = 400 ( s)
(2) Averaging processing
For channels for which averaging processing is specified, A/D conversion is
performed for the set number of times or the set amount of time. The average
value is calculated from the sum of values excluding the maximum and minimum
values, and then stored in the buffer memory.