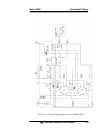
Series 4060 Installation
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 31
Table 3-1: Analog Output Connections
Pin Function
3 Channel 2, + 4-20 mA, floating
4 Channel 2, – 4-20 mA, floating
5 Channel 1, + 4-20 mA, floating
6 Channel 1, – 4-20 mA, floating
8 Channel 2, 0-1 VDC
23 Channel 2, 0-1 VDC, negative ground
24 Channel 1, 0-1 VDC
7 Channel 1, negative ground
Examples:
The analog output signal has a voltage which depends on gas
concentration relative to the full scale of the range. To relate the signal
output to the actual concentration, it is necessary to know what range the
instrument is currently on, especially when the analyzer is in the auto
ranging mode.
The signal output for concentration is linear over the currently
selected analysis range. For example, if the analyzer is set on a range
that was defined as 0-100 ppb benzene, then the output would be as
shown in Table 3-2.
To provide an indication of the range, the Range ID analog outputs
are used. They generate a steady preset voltage (or current when using
the current outputs) to represent a particular range. Table 3-3 gives the
range ID output for each analysis range.
Table 3-2: Analog Concentration Output—Example
Ppb Voltage Signal Current Signal
Benzene Output (VDC) Output (mA DC)
0 0.0 4.0
10 0.1 5.6
20 0.2 7.2
30 0.3 8.8