Total chlorine by definition is the iodine pro-
duced in a sample when it is treated with
potassium iodide at a pH between 3.5 and 4.5.
Typically, acetic acid (or vinegar) is used to
adjust the pH.
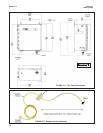
The total chlorine analyzer consists of a sam-
ple conditioning system, which injects the
reagent into the sample, and a sensor and
analyzer, which measure the amount of iodine
produced. Figure 2-1 shows the sample condi-
tioning system. The sample enters the sample
conditioning enclosure and flows to an over-
flow sampler from which the sample pump
takes suction. Excess sample drains to waste.
At the same time, the reagent pump draws
reagent, a solution of potassium iodide in
vinegar, from the reagent carboy and injects it
into the suction side of the sample pump. The
sample and reagent mix as they pass through
the pump, and total chlorine in the sample is
converted to the chemically equivalent amount
of iodine. The flow rates are 11 mL/min for the
sample and 0.2 mL/min for the reagent.
The treated sample next enters the flow cell. Bubbles injected into the flow cell produce turbulence, which
improves the stability of the reading. A membrane-covered amperometric sensor in the flow cell measures the
concentration of iodine. The analyzer receives the raw signal from the sensor and displays the concentration of
total chlorine. Display units are ppm (mg/L) chlorine as Cl
2
. The treated sample leaves the flow cell and drains
to waste along with the excess sample.
SECTION 2. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
MODEL TCL SECTION 2
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
FIGURE 2-1. Schematic of Sample Conditioning
System and Analyzer.
7