67
MODEL TCL SECTION 11
TROUBLESHOOTING
Temp. (°C) Pt 100 (Ω)
0 100.0
10 103.9
20 107.8
25 109.7
30 111.7
40 115.5
50 119.4
60 123.2
70 127.1
80 130.9
85 132.8
90 134.7
100 138.5
11.6 SIMULATING TEMPERATURE
11.6.1 General.
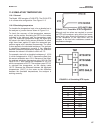
The Model 1056 accepts a Pt100 RTD. The Pt100 RTD
is in a three-wire configuration. See Figure 11-3.
11.6.2 Simulating temperature
To simulate the temperature input, wire a decade box to
the analyzer or junction box as shown in Figure 11-4.
To check the accuracy of the temperature measure-
ment, set the resistor simulating the RTD to the values
indicated in the table and note the temperature read-
ings. The measured temperature might not agree with
the value in the table. During sensor calibration an offset
might have been applied to make the measured tem-
perature agree with a standard thermometer. The offset
is also applied to the simulated resistance. The analyzer
is measuring temperature correctly if the difference
between measured temperatures equals the difference
between the values in the table to within ±0.1°C.
For example, start with a simulated resistance of 103.9
Ω, which corresponds to 10.0°C. Assume the offset from
the sensor calibration was -0.3 Ω. Because of the offset,
the analyzer calculates temperature using 103.6 Ω. The
result is 9.2°C. Now change the resistance to 107.8 Ω,
which corresponds to 20.0°C. The analyzer uses 107.5 Ω
to calculate the temperature, so the display reads
19.2°C. Because the difference between the displayed
temperatures (10.0°C) is the same as the difference
between the simulated temperatures, the analyzer is
working correctly.
FIGURE 11-3. Three-Wire RTD Configuration.
Although only two wires are required to connect
the RTD to the analyzer, using a third (and some-
times fourth) wire allows the analyzer to correct
for the resistance of the lead wires and for
changes in the lead wire resistance caused by
temperature changes.
FIGURE 11-4. Simulating RTD Inputs.