44
MODEL TCL SECTION 9
CALIBRATION
9.3 CALIBRATING TOTAL CHLORINE
9.3.1 Purpose
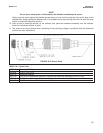
The continuous determination of total chlorine requires two steps. See Figure 9-1. First, the sample flows into a
conditioning system (the Model TCL) where it is treated with acetic acid (vinegar) and potassium iodide. The acid
lowers the pH, which allows total chlorine in the sample to quantitatively oxidize the iodide to iodine. The treated
sample then flows to the sensor. The sensor is a membrane-covered amperometric sensor, whose output is pro-
portional to the concentration of iodine. Because the concentration of iodine is also proportional to the concentra-
tion of total chlorine, the analyzer can be calibrated to read total chlorine.
Figure 9-2 shows a typical calibration curve for a total chlorine sensor. Because the sensor really measures iodine,
calibrating the sensor requires exposing it to a solution containing no iodine (zero standard) and to a solution con-
taining a known amount of iodine (full-scale standard).
The zero standard is necessary because the sensor, even when no iodine is present, generates a small current
called the residual or zero current. The analyzer compensates for the residual current by subtracting it from the
measured current before converting the result to a total chlorine value. New sensors require zeroing before being
placed in service, and sensors should be zeroed whenever the electrolyte solution is replaced. Deionized water is
a good zero standard.
Do not zero the sensor by leaving it in the
TCL flow cell and turning off reagent injec-
tion. Even though no iodine is present, the
current measured under these conditions is
not the zero current. Instead, it is the slight
response of the sensor to total chlorine in the
sample. Always use deionized water for
zeroing the sensor.
The purpose of the full-scale standard is to
establish the slope of the calibration curve.
Because stable total chlorine standards do not
exist, the sensor must be calibrated against a
test run on a grab sample of the process liquid.
Several manufacturers offer portable test kits
for this purpose. Observe the following pre-
cautions when taking and testing the grab
sample.
• Take the grab sample from a point as close
as possible to the inlet of the TCL sample
conditioning system.
• Total chlorine solutions are unstable. Run
the test immediately after taking the sam-
ple. Try to calibrate the sensor when the
chlorine concentration is at the upper end
of the normal operating range.
FIGURE 9-1. Determination of Total Chlorine
FIGURE 9-2. Sensor Current as a Function of Total
Chlorine Concentration