41
node with the same ID does not exist on the
network. Once it is determined that the ID in the
Node ID Register is unique, the software should
write a logic "1" to bit 5 of the Configuration
Register to enable the basic transmit function.
This allows the node to join the network.
The Receive Activity (RCVACT) bit of the
Diagnostic Status Register will be set to a logic
"1" whenever activity (logic "1") is detected on
the RXIN pin.
The Token Seen (TOKEN) bit is set to a logic "1"
whenever any token has been seen on the
network (except those tokens transmitted by this
node).
The RCVACT and TOKEN bits may help the
user to troubleshoot the network or the node. If
unusual events are occurring on the network,
the user may find it valuable to use the TXEN bit
of the Configuration Register to qualify events.
Different combinations of the RCVACT, TOKEN,
and TXEN bits, as shown indicate different
situations:
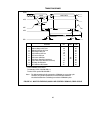
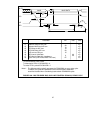
Normal Results:
RCVACT=1, TOKEN=1, TXEN=0: The node is
not part of the network. The network is
operating properly without this node.
RCVACT=1, TOKEN=1, TXEN=1: The node
sees receive activity and sees the token. The
basic transmit function is enabled. Network and
node are operating properly.
MYRECON=0, DUPID=0, RCVACT=1, TXEN=0,
TOKEN=1: Single node network.
Abnormal Results:
RCVACT=1, TOKEN=0, TXEN=X: The node
sees receive activity, but does not see the token.
Either no other nodes exist on the network,
some type of data corruption exists, the media
driver is malfunctioning, the topology is set up
incorrectly, there is noise on the network, or a
reconfiguration is occurring.
RCVACT=0, TOKEN=0, TXEN=1: No receive
activity is seen and the basic transmit function
is enabled. The transmitter and/or receiver are
not functioning properly.
RCVACT=0, TOKEN=0, TXEN=0: No receive
activity and basic transmit function disabled.
This node is not connected to the network.
The Excessive NAK (EXCNAK) bit is used to
replace a timeout function traditionally
implemented in software. This function is
necessary to limit the number of times a sender
issues a FBE to a node with no available buffer.
When the destination node replies to 128 FBEs
with 128 NAKs or 4 FBEs with 4 NAKs, the
EXCNAK bit of the sender is set, generating an
interrupt. At this point the software may
abandon the transmission via the "Disable
Transmitter" command. This sets the TA bit to
logic "1" when the node next receives the token,
to allow a different transmission to occur. The
timeout value for the EXNACK bit (128 or 4) is
determined by the FOUR-NAKS bit on the Setup
Register.
The user may choose to wait for more NAK's
before disabling the transmitter by taking
advantage of the wraparound counter of the
EXCNAK bit. When the EXCNAK bit goes high,
indicating 128 or 4 NAKs, the "POR Clear
Flags" command maybe issued to reset the bit
so that it will go high again after another count
of 128 or 4. The software may count the
number of times the EXCNAK bit goes high, and
once the final count is reached, the "Disable
Transmitter" command may be issued.
The New Next ID bit permits the software to
detect the withdrawal or addition of nodes to the
network.
The Tentative ID bit allows the user to build a
network map of those nodes existing on the