56
LifeBook S Series – Section Four
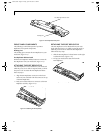
SERIAL PORT
The serial port, or COMM port, located on the Port
Replicator allows you to connect serial devices, such as
printers or scanners. In order to connect a serial inter-
face device follow these easy steps: (See figure 4-12 on
page 53 for location)
1. Align the connector with the port opening.
2. Push the connector into the port until it is seated.
3. Tighten the two hold-down screws, located on each
end of the connector.
PS/2 PORTS
The PS/2 ports located on the Port Replicator allow
you to connect an external keyboard, and/or numeric
keypad and mouse. In order to connect a PS/2 interface
device follow these easy steps: (See figure 4-12 on page 53
for location)
1. Align the connector with the port opening.
2. Push the connector into the port until it is seated.
DOCKING PORT
The docking port is used for the connection of your
notebook to an optional port replicator or docking
station. In order to connect your notebook to one of
these devices follow the instructions that came with your
docking port. (See figure 2-10 on page 12 for location)
EXTERNAL FLOPPY DISK DRIVE PORT
The external floppy disk drive port is used for attaching
an optional external floppy disk drive or an optional
modular floppy disk drive with the optional floppy
cable. In order to connect an external floppy disk drive
to your notebook follow the instructions that came with
your external floppy disk drive. Plug in an external
floppy disk drive only when the computer is turned off.
(See figure 4-12 on page 53 for location)
UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS PORT
The Universal Serial Bus port (USB) allows you to
connect USB devices such as external game pads,
pointing devices, keyboards and/or speakers. In order
to connect a USB device follow these easy steps: (See
figure 4-12 on page 53 for location)
1. Align the connector with the port opening.
2. Push the connector into the port until it is seated.
INFRARED PORT
The Infrared IrDA 1.1 (4Mbps) port allows for wireless
data transfer between your notebook and other IrDA-
compatible devices, such as another computer or a
printer, without the use of a cable. (See figure 2-9 on
page 11 for location)
It is important to keep in mind that while carrying out
this form of communication, both devices must be
placed so their infrared ports are directly facing each
other without obstruction. The devices must also be
separated by at least 6" but no more than 36" for
maximum performance.
The following conditions may interfere with infrared
communications:
■
A television, radio remote control unit, or a wireless
headphone is being used nearby.
■
Direct sunlight, fluorescent light, or incandescent light
shines directly on the port.
STEREO LINE-IN JACK
The stereo line-in jack allows you to connect an external
audio source to your notebook, such as an audio cassette
player. Your audio device must be equipped with a 1/8"
(3.5 mm) stereo mini-plug in order to fit into the stereo
line-in jack of your notebook. In order to connect a
external audio source follow these easy steps: (See
figure 2-7 on page 9 for location)
POINT
A mouse, keyboard, or keypad may be installed and
automatically recognized by your notebook without
restarting or changing setups.
POINT
Due to the ongoing changes in USB technology
and standards, not all USB devices and/or drivers
are guaranteed to work.
CAUTION
Do not move either device while communication is
active as it may interrupt data transmission.
CAUTION
Be careful not to scratch the infrared port lens. Dirt,
scratches, or other surface marks can degrade
operation.
POINT
With Windows 98 Second Edition, you can use the
Infrared Recipient application for infrared file transfers.
LapLink 2000 software can also be used for infrared file
transfers.
S Series.book Page 56 Friday, April 20, 2001 5:16 PM