6 F 3 B 0 3 6 4
31
(2) The asynchronous mode
At output: The T2/T2E/T2N writes output data to slave devices into the DN211. Disregarding the
timing of the T2/T2E/T2N's output data writing, the DN211 sends, by the scanning
cycle at the local station, written output data to a slave device. Unless output data is
updated by the T2/T2E/T2N, the DN211 sends the same data to slave devices.
At input: The DN211 receives data from slave devices by a polling response/bit strobe response.
After having received data from all slave devices, the DN211 updates input data. The
DN211 doesn't notify the completion of the data reception to the T2/T2E/T2N.
Disregarding the timing of input data update by the DN211, the T2/T2E/T2N reads
input data.
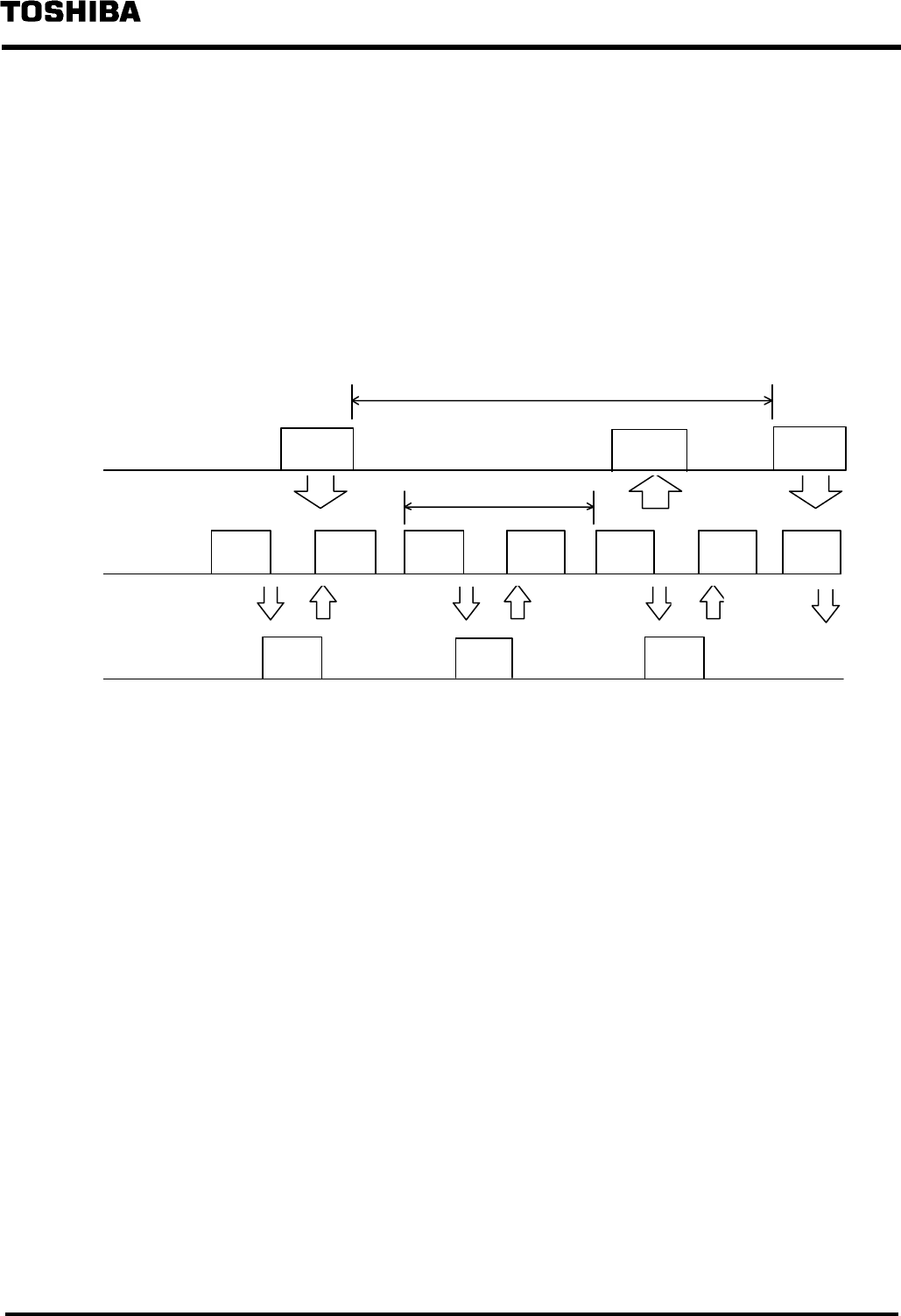
T2/T2E/T2N Data Update Cycle
DN211
Slave
T2/
T2E/
T2N
Output
data
Input
data
Output
data
Output
processing
Response
Response
Output
processing
Intput
processing
Iutput
processing
Outpu
processing
Intput
processing
Outpu
processing
Response
DN211 scan
Transfer of output data and input data between the T2/T2E/T2N ⇔ the DN211 and the transfer
between the DN211 ⇔ slave devices are asynchronous. Transfer between the T2/T2E/T2N ⇔
the DN211 are synchronizes with the scan cycle by the T2/T2E/T2N side, while the transfer
between the DN211 ⇔ slave devices are synchronizes with the scan cycle in the DN211.
Although data are secured by the byte (8 bits), the sequence program is simplified for data transfer
processing, compared with the synchronous mode. When the scan cycle by the DN211 side is
shorter than the scan cycle by the T2/T2E/T2N, delay of data update time between the
T2/T2E/T2N ⇔ slave devices becomes smaller.
The scan time by the DN211 varies depending on the number of slave devices being connected,
size of transmission data by the slave device, and the performances of the slave device being
connected.