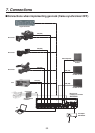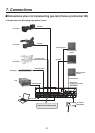
55
Appendix (glossary)
Defined below are the terms used in this manual.
Word Explanation
AB Bus
AB Bus system
A bus control mode. By executing a transition, the A bus and B bus signals are
output to the program images alternately.
Ancillary Data The auxiliary data other than the video signals which is transmitted inside the
data stream of the video serial interface. The data superimposed on the vertical
blanking period is referred to as the V ancillary data (VANC).
Aspect ratio The ratio between the horizontal and vertical dimensions of an image or screen.
It is 16:9 for the HD format and 4:3 for the SD format.
AUX
[Auxiliary Bus]
A spare bus which can be switched by signals other than the main line output
signals.
AVDL
[Automatic Video Delayline]
Automatic phase adjustment
A function to automatically adjust the input image signal phase to the horizontal
synchronization reference signal phase.
BB
Black burst
The black burst signal. A full-screen black level composite signal which is used
as the reference signal for gen-lock.
Border The area or margin that is added to the edge of a wipe or key.
Its width and color can be adjusted. The defocusing of the area around a border
is referred to as the soft effect.
Clip The threshold level of the luminance when key signals are created from a key
source.
Color Background The signals which are output from the internal color generator and used as the
background image.
Density A parameter which is used to adjust the density of the key signals.
DVI [Digital Visual Interface] A digital video interface standard.
DVI-I can handle both digital signals and analog signals.
Ethernet A computer network standard; the 10BASE-T (10 Mbps), 100BASE-TX (100
Mbps) or other such standard based on the transmission speed.
Flip Flop system A bus control mode. The signals selected by the program bus are always output
as the program images. By executing a transition, the program bus and preset
bus signals are switched over.
Frame Memory A memory which can hold the video signals equivalent to one frame.
Frame Synchronizer A function which enables the non-synchronized video signal input to be
switched.
Freeze A function which continues the display of the same image, creating the
impression that the image has been “frozen”.
Gain A parameter which adjusts the defocusing of the edges of the key signals.