114
RQT9131
Glossary
AVCHD
AVCHD is a new format (standard) for high definition video cameras
that can be used to record and play high-resolution HD images.
BD-J
Some BD-Video discs contain Java applications, and these
applications are called BD-J. You can enjoy various interactive
features in addition to playing normal video.
Bitstream
This is the digital form of multi-channel audio data (e.g., 5.1 channel)
before it is decoded into its various channels.
BONUSVIEW™
With the new play function of the BD-Video, you can enjoy the
secondary video recorded on the disc, in addition to the main movie.
CPRM (Content Protection for Recordable Media)
CPRM is technology used to protect broadcasts that are allowed to
be recorded only once. Such broadcasts can be recorded only with
CPRM compatible recorders and discs.
Decoder
A decoder restores the coded audio signals on discs to normal. This
is called decoding.
DNS Server
A server which acts like a telephone directory and translates Internet
domain names into IP addresses.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals developed by Dolby
Laboratories. Apart from stereo (2-channel) audio, these signals can
also be multi-channel audio.
Dolby Digital Plus
Multi-channel audio and higher audio quality is made possible using
Dolby Digital Plus. BD-Video supports up to 7.1 channel output.
Dolby TrueHD
Dolby TrueHD is a very high quality audio format that reproduces the
studio master audio. BD-Video supports up to 7.1 channel output.
Down-mixing
This is the process of remixing the multi-channel audio found on
some discs into fewer channels.
Drive
In the instance of this unit, this refers to the hard disk (HDD), disc
(BD) and SD card (SD). These perform the reading and writing of
data.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie theaters. There is good
separation between the channels, so realistic sound effects are
possible.
DTS-HD
DTS-HD is a high-quality, sophisticated audio format used in movie
theaters. Previous DTS Digital Surround-compatible equipment can
play DTS-HD as DTS Digital Surround audio. BD-Video supports up
to 7.1 channel output.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the lowest level of sound
that can be heard above the noise of the equipment and the highest
level of sound before distortion occurs.
Dynamic range compression means reducing the gap between the
loudest and softest sounds. This means you can listen at low
volumes but still hear dialogue clearly.
Film and video
DVD-Videos are recorded using either film or video. This unit can
determine which type has been used, then uses the most suitable
method of progressive output.
Finalise
A process that makes play of a recorded CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-R, etc.
possible on equipment that can play such media. You can finalise
BD-R, DVD-R, DVD-R DL, DVD-RW (DVD-Video format), +R, +R DL
on this unit.
After finalising, the disc becomes play-only and you can no longer
record or edit. However, finalised DVD-RW can be formatted for
recording again.
Folder
This is a place on the hard disk, disc or SD card where groups of
data are stored together. In the case of this unit, it refers to the place
where still pictures (JPEG) and MPEG2, etc. are stored.
Formatting
Formatting is the process of making media such as DVD-RAM
recordable on recording equipment.
You can format BD-RE, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW (only as DVD-Video
format), +RW, SD cards and the HDD or unused BD-R, +R and +R
DL on this unit.
Formatting permanently deletes all contents.
Frames and fields
Frames refer to the single images that constitute the video you see
on your television. Each frame consists of two fields.
≥A frame still shows two fields, so there may be some blurring, but
picture quality is generally better.
≥A field still shows less picture information so it may be rougher, but
there is no blurring.
Gateway
IP address of the electronic device providing Internet access.
Usually called a router IP address. (e.g., 192.168.0.1)
HDD (Hard disk drive)
This is a mass data storage device used in computers, etc. A disk
with a surface that has been treated with magnetic fluid is spun and
a magnetic head is brought in close proximity to facilitate the reading
and writing of large amounts of data at high speed.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
Unlike conventional connections, it transmits uncompressed digital
video and audio signals on a single cable. This unit supports high-
definition video output [720p (750p), 1080i (1125i), 1080p (1125p)]
from HDMI AV OUT terminals. To enjoy high-definition video a high
definition compatible television is required.
Hub
Used for connecting more than one device to the network.
IP address
A set of numbers which distinguish each PC on the network when,
for example, connected to the Internet. When using a PC in a LAN to
access a PC or device that is not included in the LAN, the IP address
is called the local IP address. (e.g., 192.168.0.10)
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
This is a system used for compressing/decoding colour still pictures.
If you select JPEG as the storage system on digital cameras, etc.,
the data will be compressed to 1/10–1/100 of its original size. The
benefit of JPEG is less deterioration in picture quality considering
the degree of compression.
LAN (Local Area Network)
A group of linked devices in a company, school or home.
Indicates the boundaries of a particular network.
LPCM (Linear PCM)
These are uncompressed digital signals, similar to those found on
CDs.
MPEG2 (Moving Picture Experts Group)
A standard for efficiently compressing and expanding colour video.
MPEG2 is a compression standard used for DVD and satellite based
digital broadcasting.
MPEG-4 AVC/H.264
A standard for efficiently compressing and expanding colour video.
MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 is an encoding method used for recording of
the high definition videos.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer 3)
An audio compression method that compresses audio to
approximately one tenth of its size without any considerable loss of
audio quality.
Pan&Scan/Letterbox
In general, BD-Video and DVD-Video are produced with the intention
that they be viewed on a widescreen television (16:9 aspect ratio),
so images often don’t fit regular (4:3 aspect ratio) televisions. Two
styles of picture, “Pan & Scan” and “Letterbox”, deal with this
problem.
Film: Recorded at 25 frames per second (PAL discs) or 24
frames per second (NTSC discs). (NTSC discs
recorded at 30 frames per second as well.)
Generally appropriate for motion picture films.
Video: Recorded at 25 frames/50 fields per second. (PAL
discs) or 30 frames/60 fields per second (NTSC discs).
Generally appropriate for TV drama programmes or
animation.
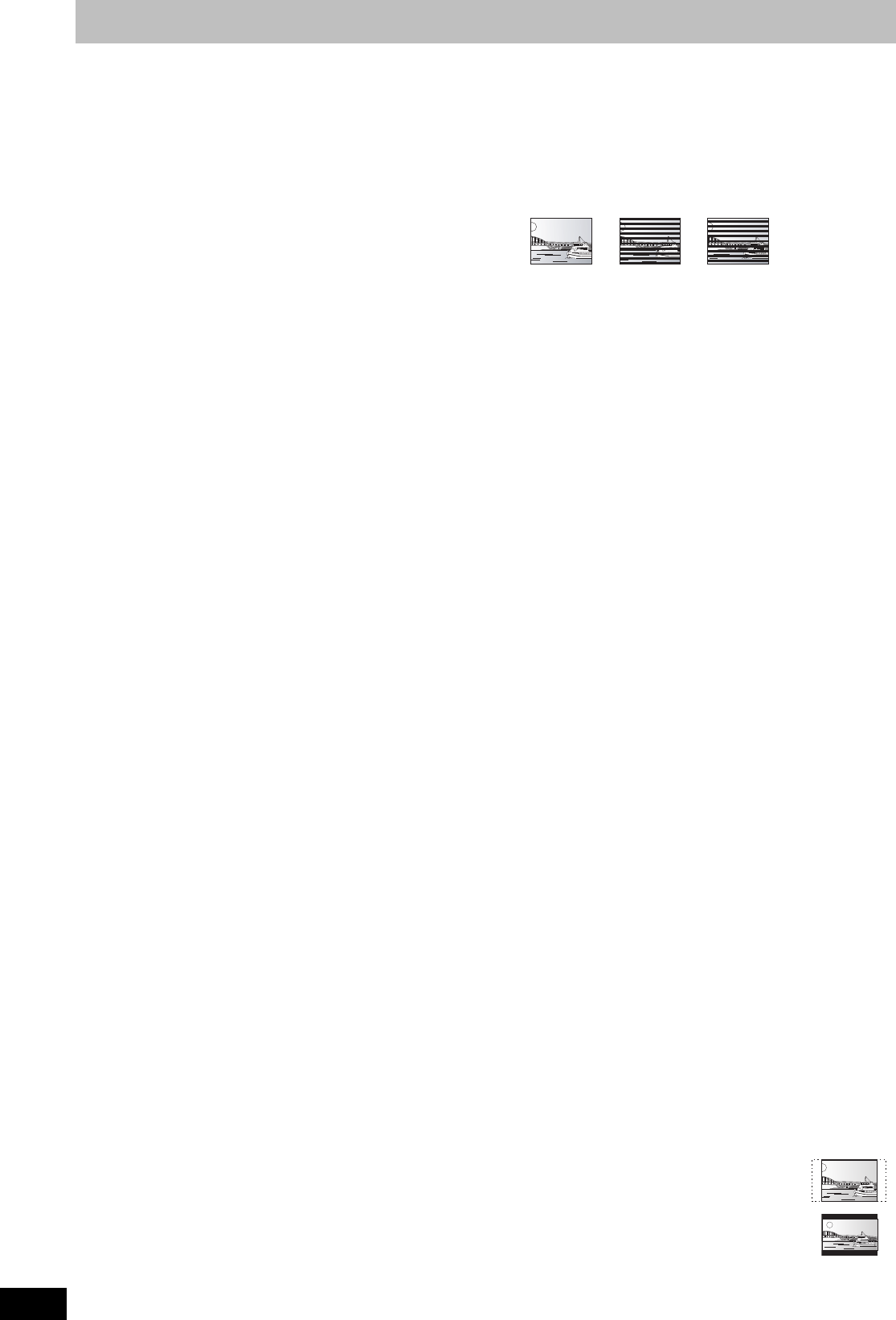
Pan & Scan: The sides are cut off so the picture
fills the screen.
Letterbox: Black bands appear at the top and
bottom of the picture so the picture
itself appears in an aspect ratio of
16:9.
u
r
Frame Field Field
DMRBW500GN-RQT9131-L_eng.book 114 ページ 2008年5月12日 月曜日 午前9時37分


















