RQT8327
53
Glossary
Bitstream
This is the digital form of multi-channel audio data (e.g., 5.1 channel)
before it is decoded into its various channels.
CPPM (Content Protection for Prerecorded Media)
A copy protection system used for DVD-Audio files. This unit
supports CPPM.
CPRM (Content Protection for Recordable Media)
CPRM is technology used to protect broadcasts that are allowed to
be recorded only once. Such broadcasts can be recorded only with
CPRM compatible recorders and discs.
Dolby Digital
This is a method of coding digital signals developed by Dolby
Laboratories. Apart from stereo (2-channel) audio, these signals can
also be multi-channel audio. A large amount of audio information can
be recorded on one disc using this method.
Down-mixing
This is the process of remixing the multi-channel audio found on
some discs into two channels for stereo output. It is useful when you
want to listen to the 5.1-channel audio recorded on DVDs through
your television’s speakers. Some discs prohibit down-mixing and this
unit can then only output the front two channels.
Tracks that do not allow down-mixing will not play correctly on
this unit except when connecting with an HDMI cable to an amplifier
that meets HDMI Ver. 1.1 standards and is CPPM compatible.
DPOF (Digital Print Order Format)
DPOF is the standard printing format for still picture data taken by a
digital camera, etc. It is used for automatic printing at a photo
developing store or on your home printer.
Drive
In the instance of this unit, this refers to the disc (DVD) and SD card
(SD). These perform the reading and writing of data.
DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
This surround system is used in many movie theaters. There is good
separation between the channels, so realistic sound effects are
possible.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the lowest level of sound
that can be heard above the noise of the equipment and the highest
level of sound before distortion occurs. Dynamic range compression
means reducing the gap between the loudest and softest sounds.
This means you can listen at low volumes but still hear dialog clearly.
Film and video
DVD-Video are recorded using either film or video. This unit can
determine which type has been used, then uses the most suitable
method of progressive output.
Film:
Recorded at 24 or 30 frames per second. Generally appropriate for
motion picture films.
Video:
Recorded at 30 frames/60 fields per second. Generally appropriate
for TV drama programs or animation.
Finalize
A process that makes play of a recorded CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-R, etc.
possible on equipment that can play such media. You can finalize
DVD-R, DVD-R DL, DVD-RW (DVD-Video format), +R or +R DL on
this unit.
After finalizing, the disc becomes play-only and you can no longer
record or edit. However, finalized DVD-RW can be formatted to
become recordable.
Folder
This is a place on the disc or memory card where groups of data are
stored together. In the case of this unit, it refers to the place where
still pictures (JPEG, TIFF) are stored.
Formatting
Formatting is the process of making media such as DVD-RAM
recordable on recording equipment.
You can format DVD-RAM, DVD-RW (only as DVD-Video format),
+R, +R DL, +RW and SD memory card on this unit.
When you use a new DVD-RW, +R, +R DL or +RW, it must be
formatted.
Formatting irrevocably deletes all contents.
Frames and fields
Frames refer to the single images that constitute the video you see
on your television. Each frame consists of two fields.
• A frame still shows two fields, so there may be some blurring, but
picture quality is generally better.
• A field still shows less picture information so it may be rougher, but
there is no blurring.
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface)
HDMI is a next-generation digital interface for consumer electronic
products. Unlike conventional connections, it transmits
uncompressed digital video and audio signals on a single cable. This
unit supports high-definition video output (720p,1080i) from HDMI
AV OUT terminal. To enjoy high-definition video a high-definition
compatible television is required.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
This is a system used for compressing/decoding color still pictures.
If you select JPEG as the storage system on digital cameras, etc.,
the data will be compressed to 1/10–1/100 of its original size. The
feature of JPEG is less deterioration in picture quality considering
the degree of compression.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer 3)
An audio compression method that compresses audio to
approximately one tenth of its size without any considerable loss of
audio quality. You can play MP3 you have recorded onto CD-R and
CD-RW.
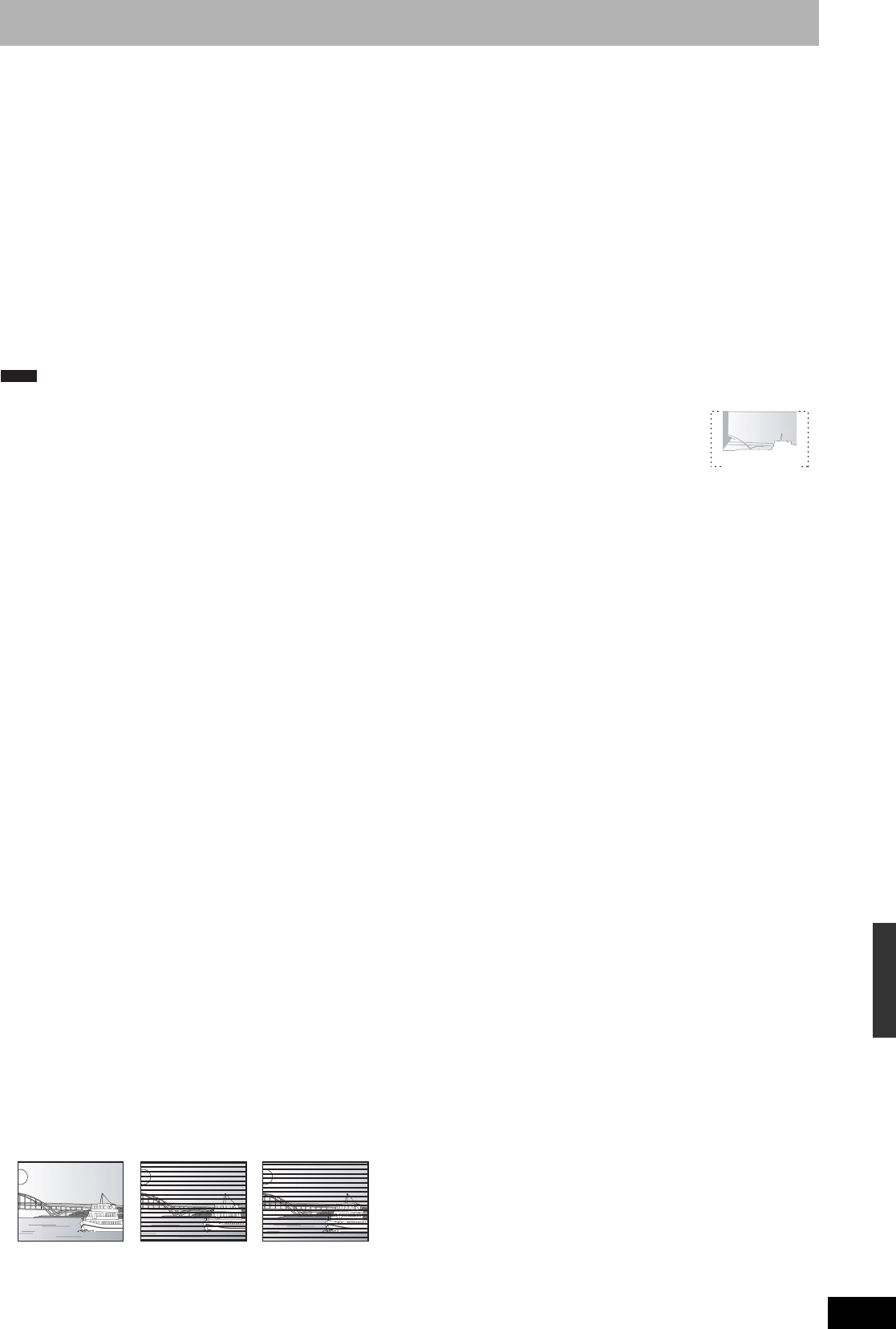
Pan & Scan/Letterbox
In general, DVD-Video are produced with the intention that they be
viewed on a widescreen television (16:9 aspect ratio), so images
often don’t fit regular (4:3 aspect ratio) televisions. Two styles of
picture, “Pan & Scan” and “Letterbox”, deal with this problem.
Playback control (PBC)
If a Video CD has playback control, you can select scenes and
information with menus.
(This unit is compatible with version 2.0 and 1.1.)
Progressive/Interlace
NTSC, the video signal standard, has 480 interlaced (i) scan lines,
whereas progressive scanning uses twice the number of scan lines.
This is called 480p.
Using progressive output, you can enjoy the high-resolution video
recorded on media such as DVD-Video. Your television must be
compatible to enjoy progressive video.
Protection
You can prevent accidental deletion by setting writing protection or
deletion protection.
Sampling frequency
Sampling is the process of converting the heights of sound wave
(analog signal) samples taken at set periods into digits (digital
encoding). Sampling frequency is the number of samples taken per
second, so larger numbers mean more faithful reproduction of the
original sound.
Thumbnail
This refers to a miniature representation of a picture used to display
multiple pictures in the form of a list.
TIFF (Tag Image File Format)
This is a system used for compressing/decoding color still pictures.
A common format for storing high quality images on digital cameras
and other devices.
1080i
In one high definition image, 1080 alternating scan lines pass every
1/60
th
of a second to create an interlace image. Because 1080i more
than doubles current television broadcasts of 480i, the detail is much
clearer and creates a more realistic and rich image.
720p
In one high definition image, 720 scan lines pass at the same time
every 1/60
th
of a second to create a progressive image. Since
progressive video does not alternate scan lines like interlace, there
is a minimal amount of screen flicker.
DVD-A
=
+
Frame Field Field
Pan & Scan:The sides are cut off so the picture
fills the screen.
Letterbox: Black bands appear at the top and
bottom of the picture so the picture
itself appears in an aspect ratio of
16:9.