Operating modes and functions
ELSA MicroLink Cable
37
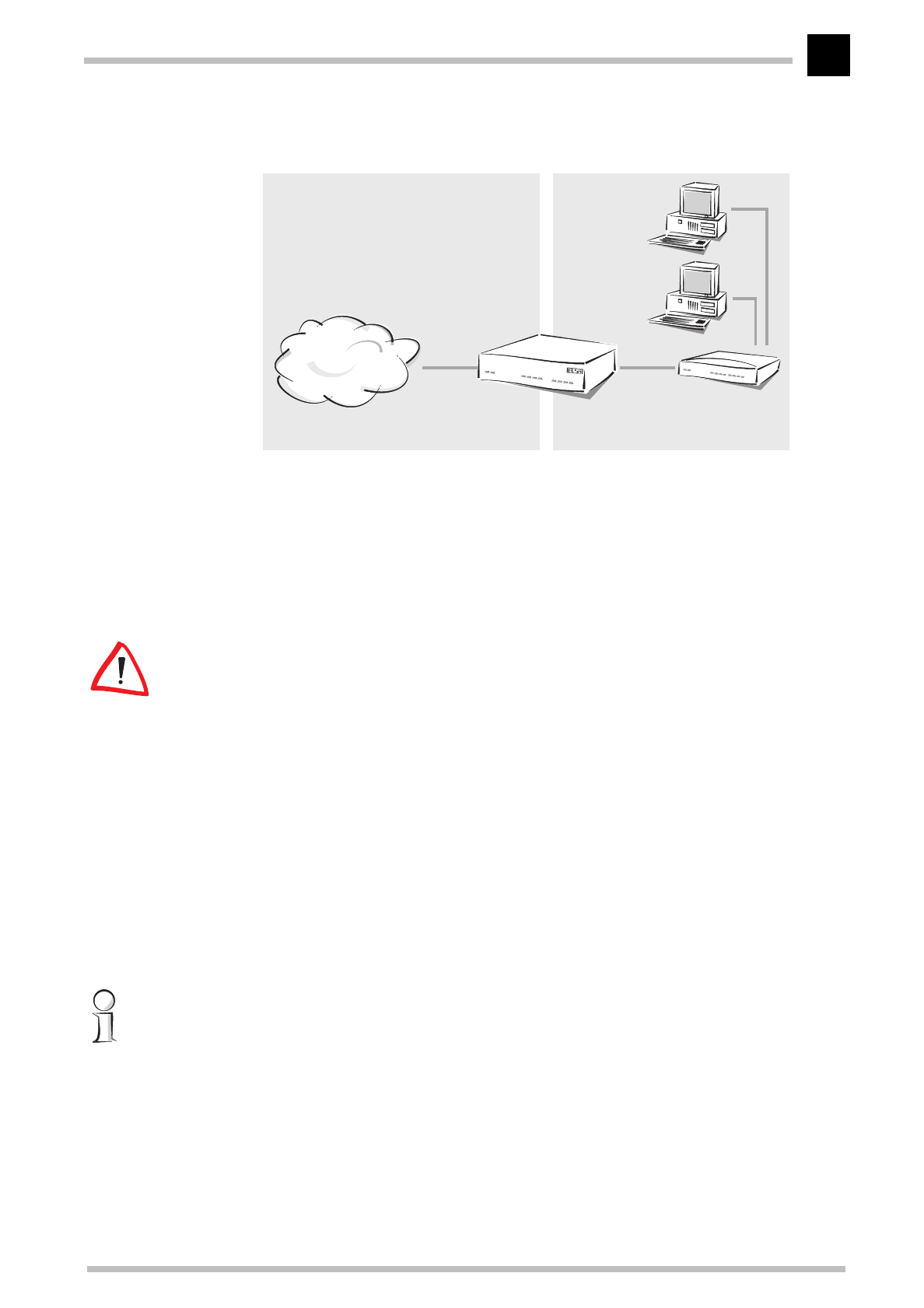
The cable modem is therefore assigned a cable IP address and a LAN IP address, each
with its own appropriate network mask. Use the 'Masquerade' option to inform the cable
modem which of the two addresses to use when transferring the packets.
'Off': No masquerading.
'on': Use this entry to apply the cable IP address that was assigned during the
registration at the headend by the network operator.
If the cable modem is used as an IP router without masquerading, make sure that IP/RIP
is enabled. When using it as an IP router with masquerading, IP/RIP should be disabled.
How does IP masquerading work?
Masquerading makes use of a characteristic of TCP/IP data transmission, which is to use
port numbers for destination and source as well as the source and destination addresses.
When the router receives a data packet for transfer it now notes the IP address and the
sender's port in an internal table. It then gives the packet its unique cable IP address
and a random new port number. It also enters this new port on the table and forwards
the packet with the new information.
The response to this new packet is now sent to the cable IP address of the cable modem
with the new sender port number. The entry in the internal table allows the router to
assign this response to the original sender again.
You can view these tables in detail in the router statistics (see also 'Status').
Simple and inverse masquerading
This masking operates in both directions: The local network behind the cable IP address
of the router is masked if a computer from the LAN of the user sends a packet to the
Internet (simple masquerading).
If, on the other hand, a computer sends a packet from the Internet to, for example, an FTP
server on the LAN, from the point of view of this computer the router appears to be the
MCNS
Cable TV net-
work
ELSA MicroLink
Cable
Hub
LAN of the user
Cable IP address LAN IP address


















