Operating modes and functions
ELSA MicroLink Cable
39
Initially the router checks whether a DNS server has been entered in its own
settings (in configuration tool
ELSA LANconfig
in the 'TCP/IP' configuration section
on the 'Addresses' tab or in the /
Setup/TCP-IP Module
menu). If it finds it
there, it will then retrieve the desired information from this server.
If no DNS server has been entered in the cable modem, it tries to reach the network
operator's DNS server to retrieve the IP address associated with the name. The
address of the DNS at the network operator is transferred during the registration of
the cable modem by the headend.
This procedure does not require you to have any knowledge of the DNS server address.
Entering the LAN IP address of the cable modem as the DNS server for the workstation
computers is sufficient to enable name associations. This procedure also automatically
updates the address of the DNS server. Your local network always receives the most
current information even if, for example, the provider sending the address changes the
name of his DNS server or you change to another provider.
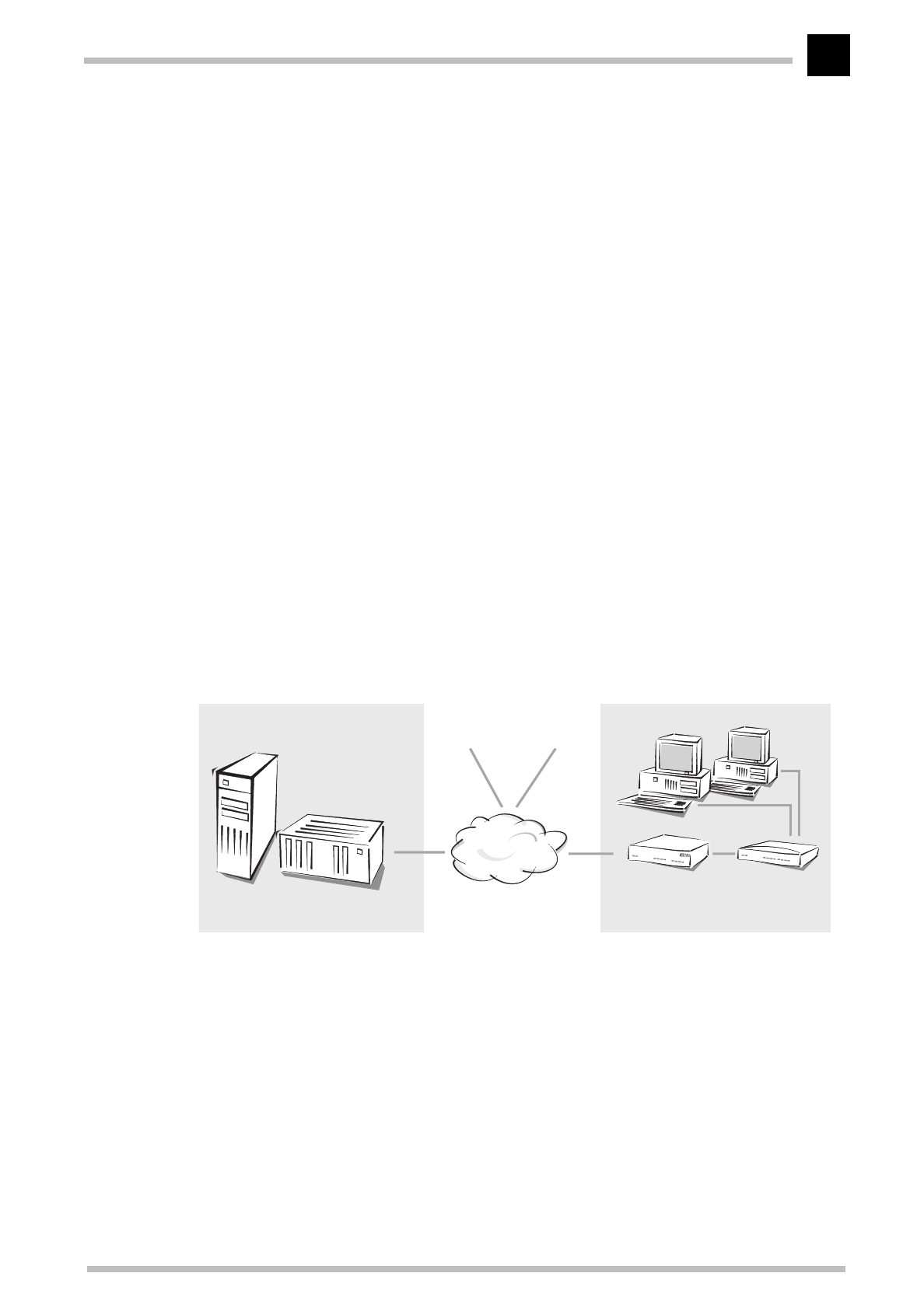
Bridging
A bridge connects two or more LANs in such a way that they appear to be a single large
network. When bridging via cable modems, the LAN of the cable network operator with
the headend is on one side and the LAN of the network participants with the cable
modem and the local workstations on the other.
In the bridge operating mode, the
ELSA MicroLink Cable
transfers all data to computers
without locally assigned MAC addresses, between the local network or another local
area network (LAN) or a workstation on one side and the cable network on the other side.
The bridge thus learns on its own which MAC addresses are located on its own network
and which are located on the other side. After a very high level of data traffic that occurs
during the initial negotiations between the two LANs, the network load drops sharply.
When receiving data from the cable network, the bridge in the cable modem uses the
MAC addresses to determine whether the data is destined for its own LAN. The bridge
will only accept data packets that are addressed to MAC addresses in its LAN.
MCNS
Headend
Cable TV net-
work
ELSA MicroLink
Cable
Hub
LAN of the cable network ope-
rator
LAN of the user
further connected cable
modems


















