Technical basics
ELSA MicroLink Cable
51
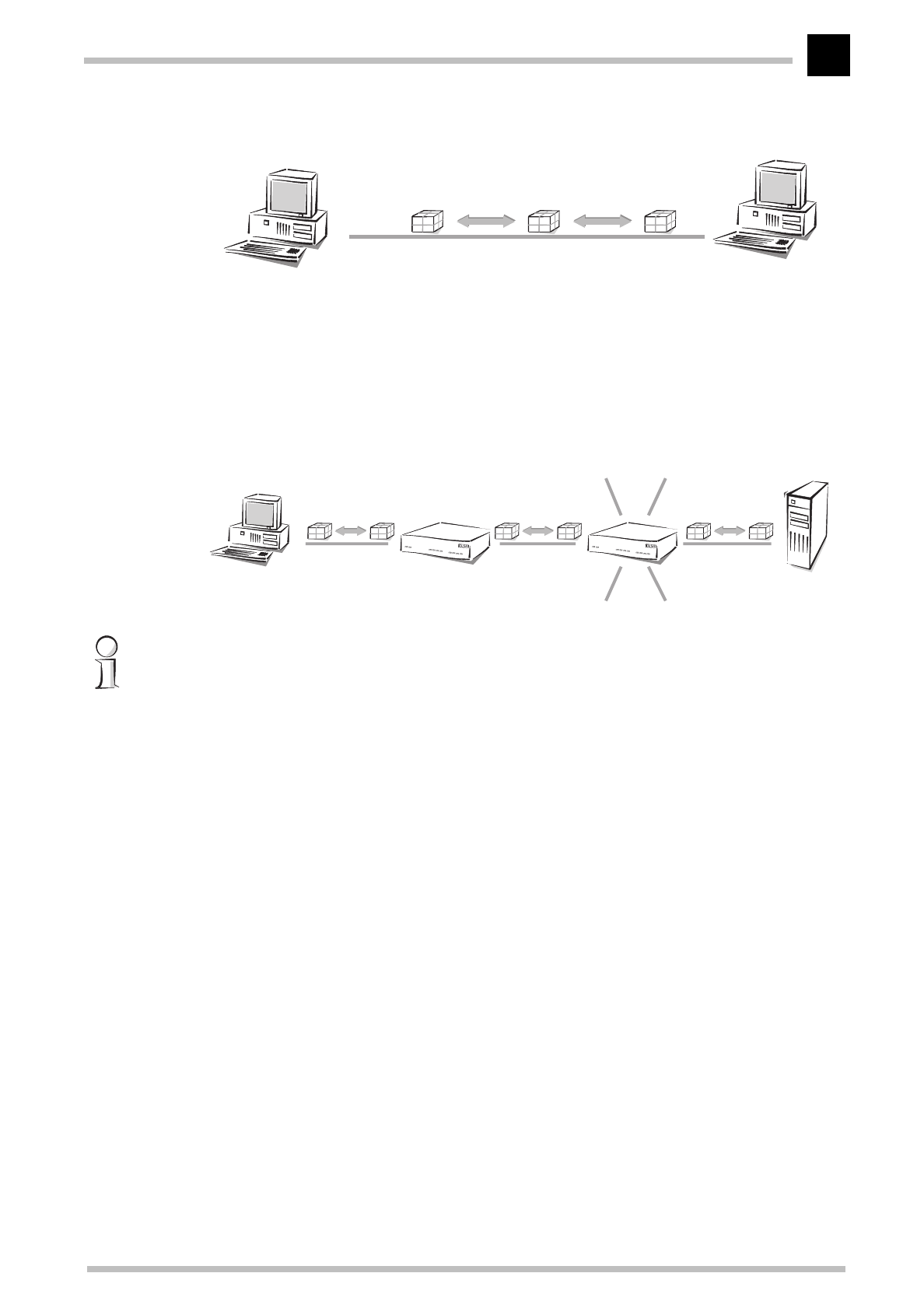
Access to the Internet is also established through point-to-point connections. Even
though the data packets are sent from the host at the Internet user to the host at the
Internet provider (server) via several routers, every data packet still has its own specific
destination. Furthermore, the routers will only forward the data packets to one recipient.
That's why we also call this connection unambiguous.
Strictly speaking, the term “point-to-point connection” is not quite correct. For our
purposes though, it is sufficient to distinguish this kind of connection from the following
“point-to-multipoint connections”.
Point-to-
multipoint
connection
Generally speaking, it would be uneconomical to directly connect all computers in a
network via point-to-point connection cables, as the computers would then require
multiple interfaces. Computers in a network are therefore plugged into a joint medium
shared by all hosts. The sender simply sends its packet with instructions concerning the
recipient to the medium to which other hosts are connected. The data packet arrives at
every host in the network. Each host then decides whether it is the recipient of the
packet or not. If the packet is addressed to the corresponding host, it will then accept it.
If not, the host will ignore (reject) it. This is a“point-to-multipoint connection”, since we
are not dealing with an unambiguous connection.
Host Host
Medium
Data packet
Host Host
Internet user Web server
Connections to other
routers
Router


















