Technical basics
ELSA MicroLink Cable
56
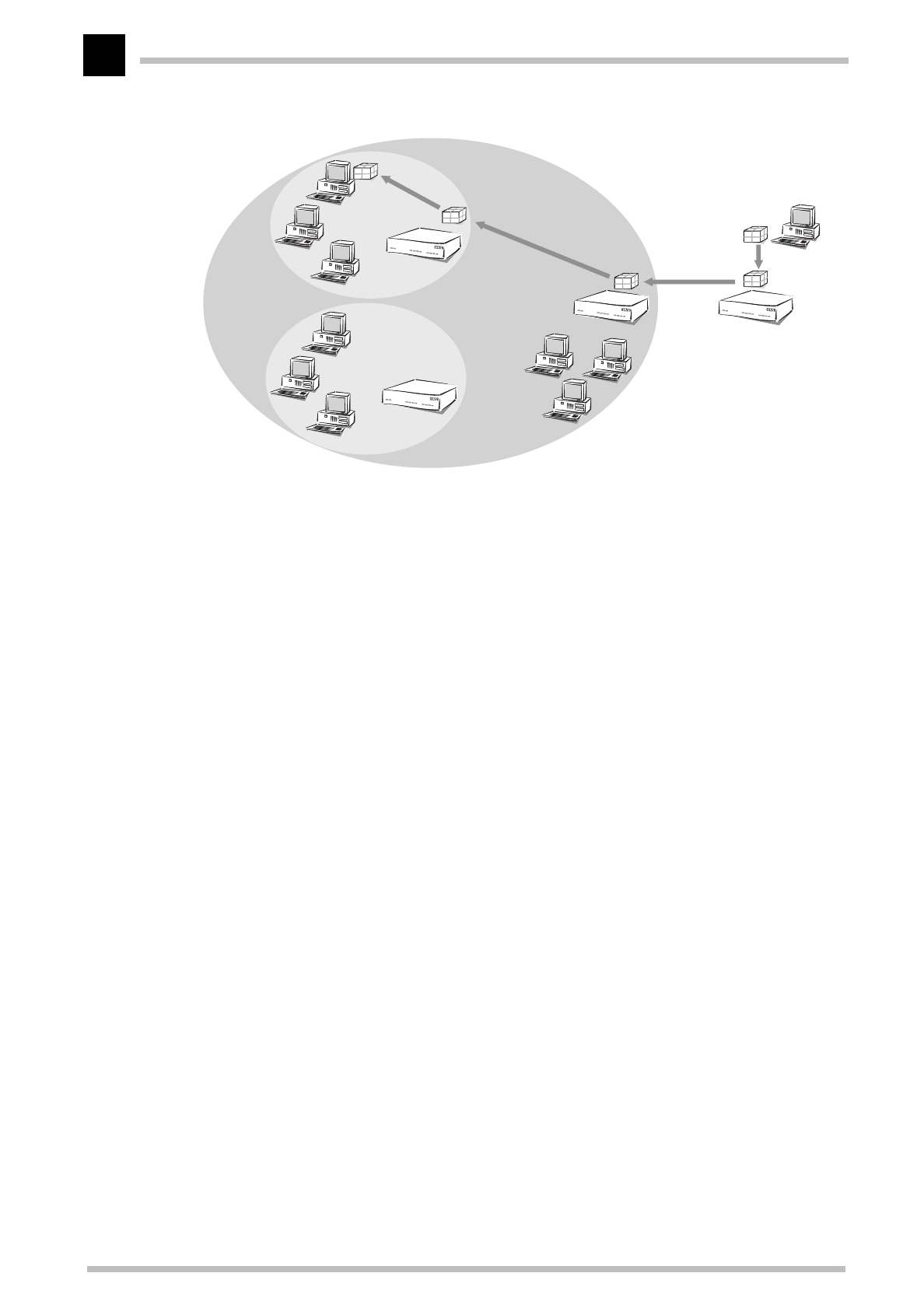
As an example, think of a company with one large network, in which the different
divisions are incorporated as small subnets. The address of the network for the
marketing division is made up hierarchically from the address of the company and that of
the department.
Whenever a host external to the company network sends a packet to a host in the
Example Inc., this is what happens:
ቢ The sender gives the packet the destination address “host 'Smith' – Marketing –
Example Inc.”.
ባ All an external router that establishes the connections to other networks has to
know is how to reach Example Inc. As soon as it receives a packet with the address
for Example Inc., it passes the packet on to the router responsible for Example Inc.
ቤ The router at Example Inc. receives the packet and extracts from the address the
information that it is directed at Example Inc. Since it is itself part of Example Inc.,
it takes a closer look at the address to find the name of the division. It then passes
the packet on to the router in the marketing division.
ብ The router in the marketing division receives the packet and extracts from the
address the information that it is directed at the marketing division of Example Inc.
Since it is itself part of this division, it takes a closer look at the address to find the
name of the host. It then passes the packet on to the host of the employee Sam
'Smith'.
Now we shall take a look at the example using proper IP addresses instead of symbolic
names. The network of Example Inc. has the numerical space '192.168.100.0' to
'192.168.100.255' at its disposal, with the '0' for the network address and the '255' for
the sender address.
Marketing
Development
Superordinate
network:
Example Inc.
External router as a
connection to other net-
works
Host 'Smith'
Example
Inc.'s router
External host