Technical basics
ELSA MicroLink Cable
48
computer. On the other side is the operator of the broadband cable network who would
like to provide more than just radio and TV.
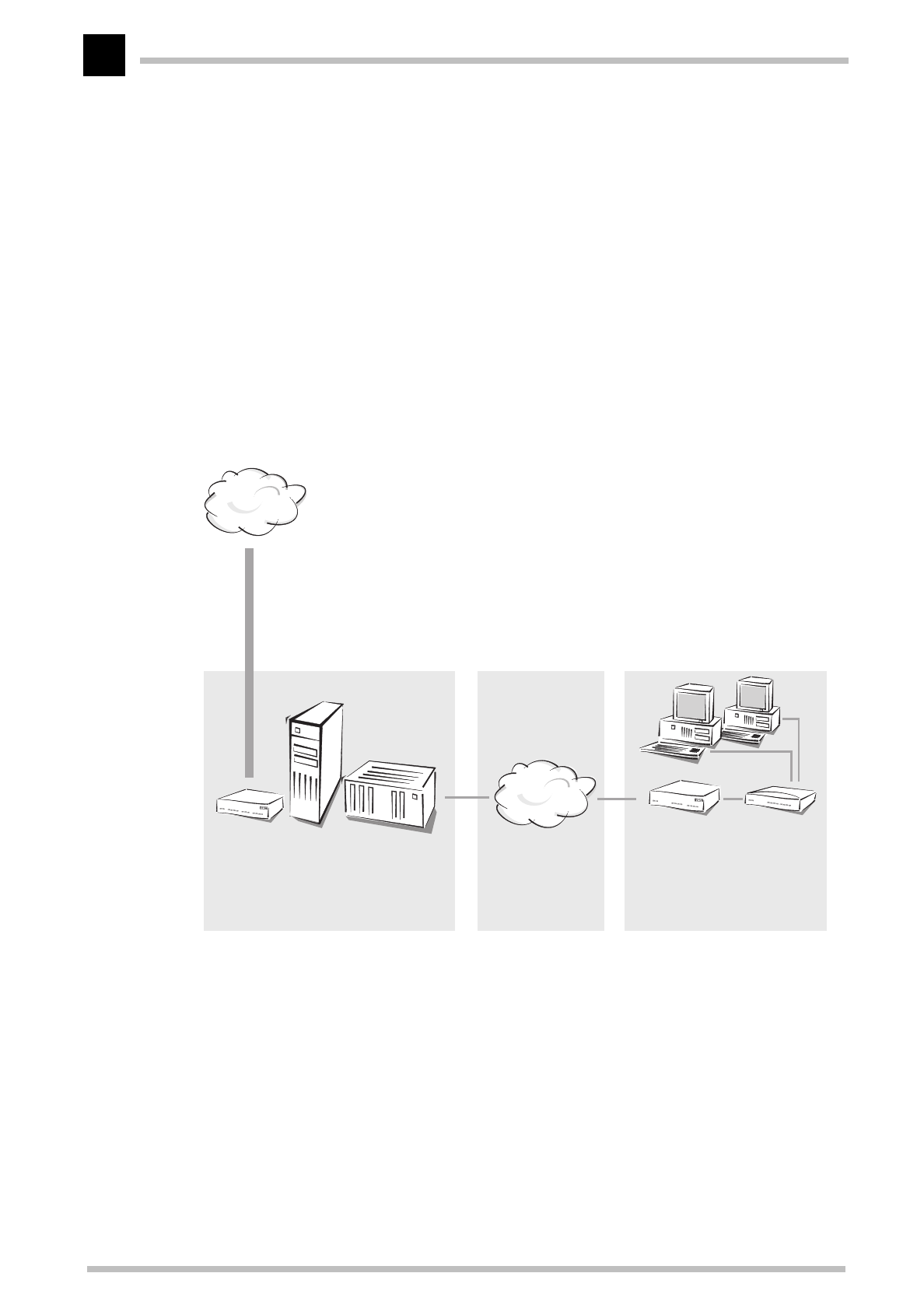
A headend can accommodate up to 2000 individual users with cable modems like the
ELSA MicroLink Cable
. The headend functions as a multiport, however, giving every user
access to the cable network at any time. Unlike access through analog or ISDN modems,
there are no connection attempts that could fail because all of the provider's ports are
already in use. No further hardware is needed for the connection between the Internet
user and the network operator as long as both the cable modem and the headend use the
bidirectional MCNS standard.
On the other side, the network operator has to establish a connection to the Internet. He
can either act as an Internet service provider (ISP) himself and directly establish access
to the Internet, or he can outsource this task on to another ISP or an online service.
This connection to the backbone is of little relevance to the user. However, the greater
the performance of the network operator's backbone line, the quicker the users receive
information from the Internet.
Registration in the cable network
In comparison to other data transfer media, the cable TV network has a very high
bandwidth at its disposal—thus the term broadband cable network. The full bandwidth
is divided up into a variety of channels that are reserved for the transmission of different
kinds of information. You know this from television, where you also find different
Internet
MCNS
Server with
DHCP
Headend
Cable TV net-
work
ELSA MicroLink
Cable
Computer workstation in
LAN
Hub
Backbone
Network of the cable network
o
p
erator
Network of the user


















