118
Using UMID Data
Appendix
Using UMID Data
Metadata is additional information recorded on discs along
with audio-visual data. It is used to bring greater efficiency
to the flow of operations from material acquisition through
editing, and to make it easier to find and reuse material.
As one of application of metadata, the UMID has been
internationally standardized.
What is a UMID?
A UMID (Unique Material Identifier) is a unique identifier
for audio-visual material defined by the SMPTE 330M-
2003 standard.
A UMID may be either as a 32-byte Basic UMID or an
Extended UMID, which includes an additional 32 bytes of
Source Pack to make a total 64 bytes.
For details, refer to SMPTE 330M.
A globally unique ID is automatically recorded for every
clip.
The Extended UMID is metadata that provides additional
information such as location, time/date, company ID and
so on.
The UMID is applied as follows.
Using the Extended UMID
You have to enter a country code, organization code and
user code. Set the country code referring to the table in ISO
3166, and set the organization code and user code
according to the guidelines of your organization.
For details, see “Setting UMID ownership information”
(page 119).
Functions of UMID data
UMID data enables the following:
• Addition of a globally unique ID to every clip of audio-
visual material. The unique ID is used to detect the
material source and to link it with the original source
material.
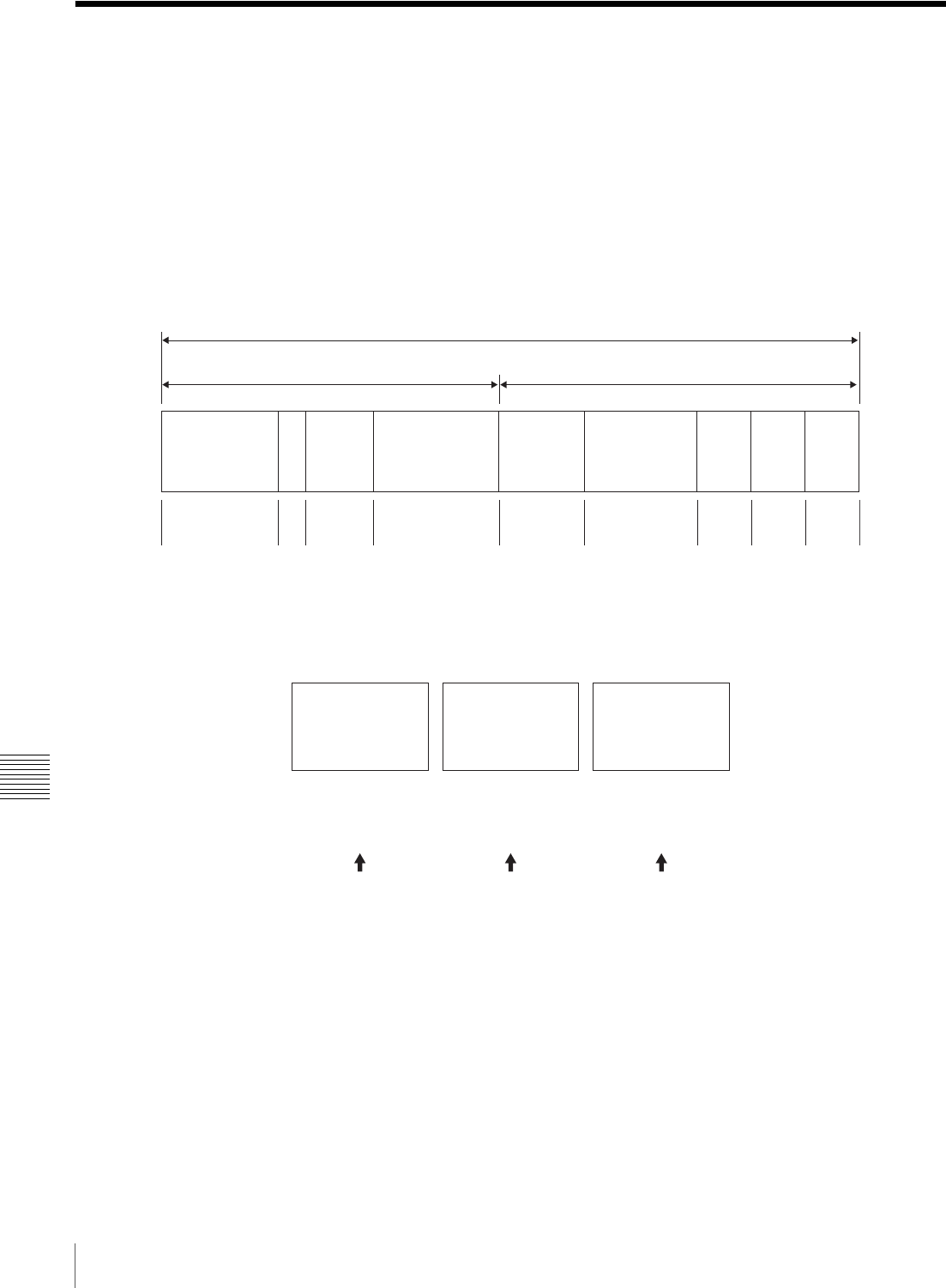
Extended UMID (64 bytes)
Basic UMID (32 bytes) Source Pack (32 bytes)
Universal label L
Instance
No.
Material Number
Time/Date
Spatial
Coordinates
Country
Org User
12 bytes
1
3 bytes
16 bytes
8 bytes 12 bytes
4 bytes 4 bytes 4 bytes
Instance No.
Material No.
ID generated when
shooting
Same as the above
Source Pack
Shooting
information (when,
where and who)
Same as the above
Original material: 00 00 00
Copied material: generation number (1 byte)
+ random number (2 byte)
Distinguish between the
original material and copied
material
Material source ID/
detecting material
Metadata pack that
identifies the source of
material unit by defining the
when, where and who of
the material unit with which
it is associated.


















