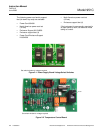
Instruction Manual
748214-V
June 2009
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Installation 2-5
Model 951C
2-5 GAS REQUIREMENTS
The instrument requires two gases normally
supplied from cylinders. They are:
a. Air (U.S.P. Breathing Grade)
This is used as both (a) an oxygen source
for generation of the ozone required for the
chemiluminescence reaction, and (b) a
standard gas for zero calibration (nitrogen
can also be used). Gas for each purpose
must be supplied from a separate cylinder
due to different pressure requirements at
ozonator and zero inlets.
b. Span Gas
This is a standard gas of accurately known
composition, used to set an upscale calibra-
tion point. The usual span gas is NO or NO
2
in a background of nitrogen.
WARNING
HIGH PRESSURE GAS CYLINDERS
This instrument requires periodic calibration
with a known standard gas. See Section 3-3.
See also General Precautions for Handling
and Storing High Pressure Gas Cylinders,
page P-5.
NOTE
For maximum calibration accuracy, the
concentration of NO in the span gas
should be similar to that in the sample
gas. Also, the span gas should be
supplied to the rear panel SAMPLE inlet
at the same pressure as the sample gas.
To ensure constant pressure, a pressure
regulator may be utilized immediately
upstream from the SAMPLE inlet.
Each gas used should be supplied from a
tank or cylinder equipped with a clean,
non-corrosive type, two-stage regulator. In
addition, a shut-off valve is desirable. Install
the gas cylinders in an area of relatively
constant ambient temperature.
2-6 SAMPLE REQUIREMENTS
The sample must be clean and dry before
entering the analyzer. In general, before
admission to the analyzer, the sample
should be filtered to eliminate particles lar-
ger than two microns and have a dew point
below 90°F (32°C). The factory can provide
technical assistance if desired.
Proper supply pressure for sample, zero
and span gases for the Model 951C is
20 psig (138 kPa).
2-7 GAS CONNECTIONS
WARNING
TOXIC AND OXIDIZING GAS HAZARDS
This instrument generates ozone which
is toxic by inhalation and is a strong
irritant to throat and lungs. Ozone is
also a strong oxidizing agent. Its
presence is detected by a characteristic
pungent odor.
The instrument exhaust contains both
ozone and nitrogen dioxide, both toxic
by inhalation, and may contain other
constituents of the sample gas which
may be toxic. Such gases include
various oxides of nitrogen, unburned
hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide and
other products of combustion reactions.
Carbon monoxide is highly toxic and can
cause headache, nausea, loss of
consciousness, and death.
Avoid inhalation of the ozone produced
within the analyzer and avoid inhalation
of the sample and exhaust products
transported within the analyzer. Avoid
inhalation of the combined exhaust
products at the exhaust fitting.
Keep all tube fittings tight to avoid leaks.
See Section 2-8 for Leak Test Procedure.
Connect rear exhaust outlet to outside
vent by a 1/4 inch (6.3 mm) or larger
stainless steel or Teflon line. Check vent
line and connections for leakage.