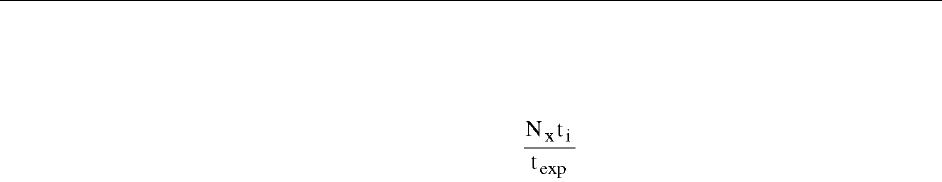
Chapter 9 Exposure and Readout 69
digitized. The percentage of smearing is given by the equation below, simply the time
needed to shift all rows from the imaging area divided by the exposure time.
(6)
Digitization
During readout, an analog signal representing the charge of each pixel (or binned group
of pixels) is digitized. The number of bits per pixel is based on both the hardware and the
settings programmed into the camera through the software. The I-PentaMAX can contain
up to two A/D converters with different readout rates settable through software.
Dual A/D Converters Option
There is provision in the I-PentaMAX Camera for two complete analog channels
including separate A/D converters to provide optimum signal-to-noise ratios at both
readout speeds. Because the readout noise of CCD arrays increases with the readout rate,
it is sometimes necessary to trade off readout speed for high dynamic range. Although
slowing the readout speed of a high-speed A/D converter gives some relief, a fast A/D
converter will always be noisier than one designed for optimum noise performance. Only
the I-PentaMAX Camera with its two analog channels, one optimized for high speed, the
other for high precision, provides a completely satisfactory solution to this problem. For
the most common system configurations, there will be a 5 MHz converter for the fastest
possible data collection, and a 1 MHz converter for use where imaging with lower noise
is desired. Switching between the channels is completely under software control for total
experiment automation.


















