68
RQTV0134
Glossary
Bitstream
This is a signal compressed and converted into digital form. It is
converted back to a multi-channel audio signal, e.g., 5.1-channel, by
a decoder.
CPRM (Content Protection for Recordable Media)
CPRM is technology used to protect broadcasts that are allowed to
be recorded only once. Such broadcasts can be recorded only with
CPRM compatible recorders and discs.
Decoder
A decoder restores the coded audio signals on DVDs to normal. This
is called decoding.
Down-mixing
This is the process of remixing the multi-channel audio found on
some discs into two channels. It is useful when you want to listen to
the 5.1-channel audio recorded on DVDs through your TV’s
speakers. Some discs prohibit down-mixing. If this is the case, this
unit can only output the front two channels.
Dynamic range
Dynamic range is the difference between the lowest level of sound
that can be heard above the noise of the equipment and the highest
level of sound before distortion occurs. Dynamic range compression
means reducing the gap between the loudest and softest sounds.
This means you can hear dialog clearly at low volume.
Film and Video
DVD-Videos are recorded using either film or video. The unit can
determine which type has been used, then uses the most suitable
method of progressive output.
≥Film is 24 or 30 frames per second, with motion picture film
generally being 24 frames per second.
≥Video is 60 fields per second (2 fields making up 1 frame).
Finalize
A process that makes play of a recorded CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-R,
etc. possible on equipment that can play such media. You can
finalize DVD-R, DVD-R DL, DVD-RW (DVD-Video format), +R and
+R DL on the unit. After finalizing, the disc becomes play-only and
you can no longer record or edit. However, finalized DVD-RW can
be formatted to become recordable.
Formatting
Formatting is the process of making media such as DVD-RAM
recordable on recording equipment.
You can format DVD-RAM, DVD-RW (only as DVD-Video format)
and +RW on the unit.
Formatting irrevocably erases all contents on the disc.
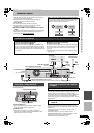
Frame and field
Frame refers to the single images that constitute the video you see
on your TV. Each frame consists of 2 fields.
Frame Field Field
≥A frame still shows 2 fields, so there may be some blurring
between them, but picture quality is generally better.
≥A field still shows less picture information so it may be rougher, but
there is no blurring.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
This is a system used for compressing/decoding color still pictures. If
you select JPEG as the storage system on digital cameras, etc., the
data will be compressed to 1/10–1/100 of its original size. The
benefit of JPEG is less deterioration in picture quality considering
the degree of compression.
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer 3)
An audio compression method that compresses audio to
approximately one-tenth of its size without any considerable loss of
audio quality. You can play MP3s you have recorded onto CD-R and
CD-RW.
Pan & Scan/Letterbox
In general, DVD-Video are produced with the intention that they will
be viewed on a widescreen TV (16:9 aspect ratio), so images often
don’t fit regular TVs (4:3 aspect ratio). 2 styles of picture,
“Pan & Scan” and “Letterbox”, deal with this problem.
Pan & Scan: The sides are cut off so the picture fills the screen.
Letterbox: Black bands appear at the top and bottom of the
picture so the picture itself appears in an aspect
ratio of 16:9.
Playback control (PBC)
If a Video CD has playback control, you can select scenes and
information with menus displayed on the screen.
(The unit is compatible with version 2.0 and 1.1.)
Progressive/Interlace
NTSC, the video signal standard, has 480 interlaced (i) scan lines,
whereas progressive scanning uses twice the number of scan lines.
This is called 480p.
Using progressive output, you can enjoy the high-resolution video
recorded on media such as DVD-Video.
Your TV must be compatible to enjoy progressive video.
Protection
You can prevent accidental erasure by setting writing protection or
erasure protection.
Sampling frequency
Sampling is the process of converting the heights of sound wave
(analog signal) samples taken at set periods into digits (digital
encoding). Sampling frequency is the number of samples taken per
second, so larger numbers mean more faithful reproduction of the
original sound.
Thumbnail
This refers to a miniature representation of a picture used to display
multiple pictures in the form of a list.
TIFF (Tag Image File Format)
This is a system used for compressing/decoding color still pictures, a
common format for storing high quality images on digital cameras
and other devices.
=
+
M6VP&PC.book 68 ページ 2006年2月6日 月曜日 午後3時20分