Chapter 5. Application Developer XML Tools 91
If you review the generated XML file, you will notice that the root element is
qualified to belong to the target namespace specified in the schema file. It is also
important to note that the local elements that belong to the root element are
unqualified. That is, they do not have a prefix. This is because the schema file by
default specifies that local elements should not be qualified.
In order to qualify all the local elements in an XML document, the XML Schema
must set the elementFormDefault attribute to
qualified in the schema element.
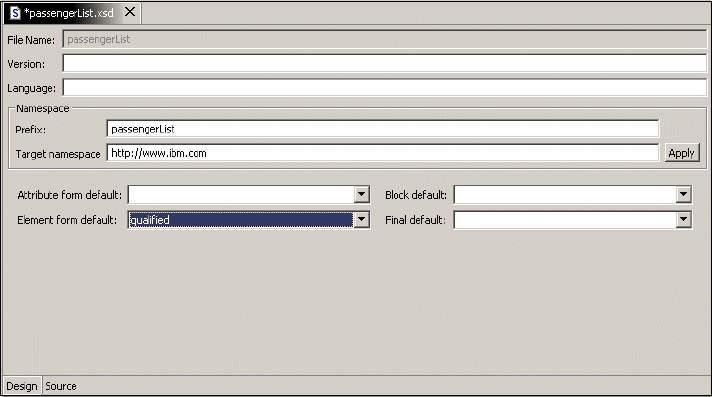
This can be accomplished by selecting Qualified in the Element form default
field of the Design view for the schema, as shown in Figure 5-8. All XML files
created from this schema will have all the elements qualified with the namespace
prefix.
Figure 5-8 Indicate all local elements to be qualified.
When you use the XML Schema editor to create your schema file by default, the
target namespace for this schema is http://www.ibm.com as indicated by the
target namespace attribute, as shown in Figure 5-8. If you do not specify a prefix
in the prefix field for the schema object, then you are making the default
namespace for this schema to be the same as the target namespace. When you
click the Apply button, you will notice that the xmlns attribute is added to the
schema tag to indicate that the default namespace of this schema is
http://www.ibm.com. You will also notice that the XML Schema constructs will
automatically be qualified with the prefix xsd to distinguish them from the types
that are in the default namespace. By making the target namespace of this
schema the default namespace, you do not have to qualify types from this
schema when you reference them.


















