Wiring and Noise Reduction Methods 483Appendix E
Appendix E
Wiring and Noise Reduction Methods
Separating Digital and Analog SCP Signals
Signals with very fast rise time can cause interference with nearby signal
paths. This is called cross-talk. Digital signals present this fast rise-time
situation. Digital I/O signal lines that are very close to analog input signal
lines can inject noise into them.
To minimize cross-talk, maximize the distance between analog input and
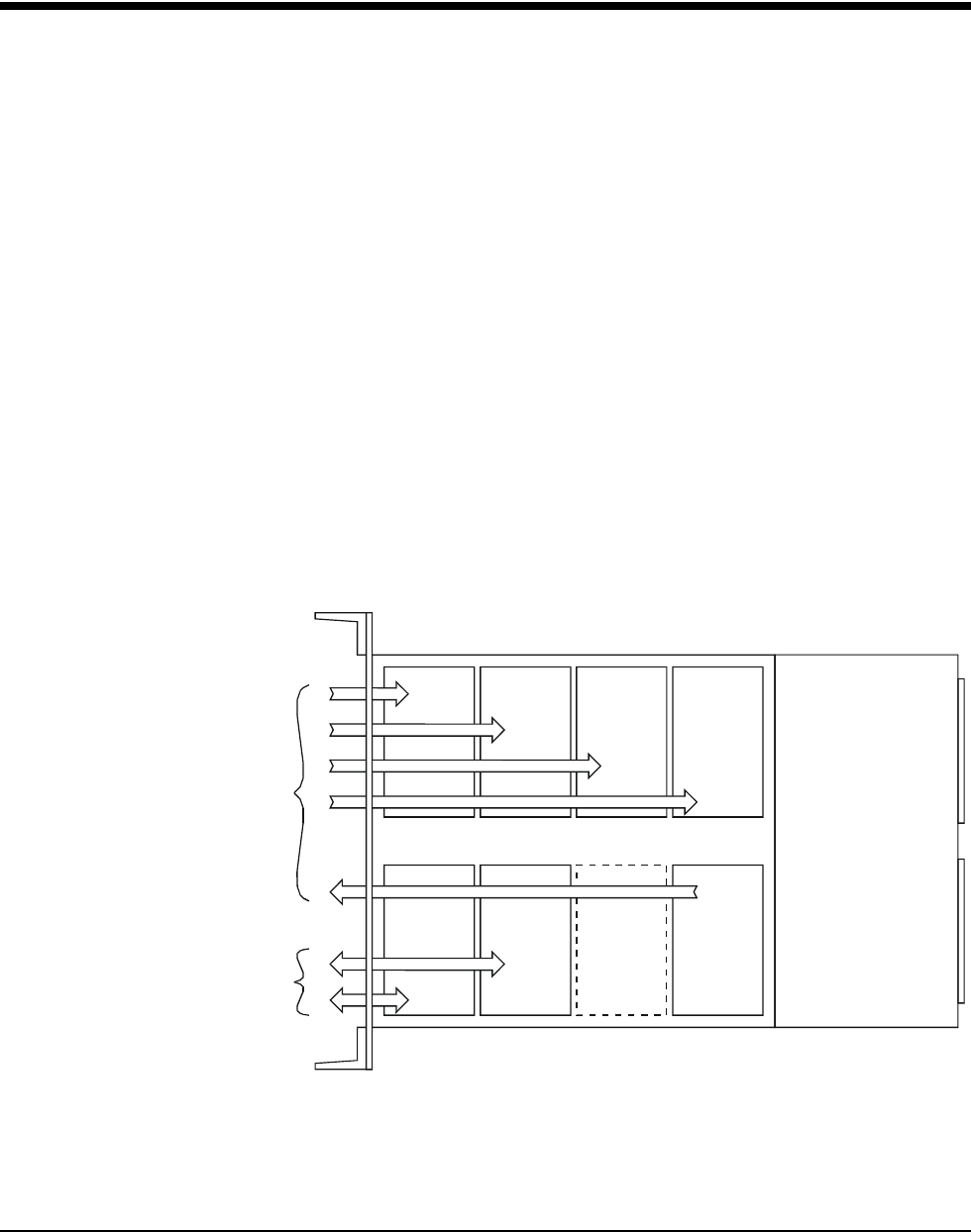
digital I/O signal lines. By installing analog input SCPs in positions 0
through 3 and digital I/O SCPs in positions 4 through 7, these types of
signals are kept separated by the width of the VT1422A module. The signals
are further isolated because they remain separated on the connector module
as well. Note that in Figure E-1, even though only seven of the eight SCP
positions are filled, the SCPs present are not installed contiguously, but are
arranged to provide as much digital/analog separation as possible.
If it is necessary to mix analog input and digital I/O SCPs on the same side,
the following suggestions will help provide quieter analog measurements.
• Use analog input SCPs that provide filtering on the mixed side.
• Route only high level analog signals to the mixed side.
Figure E-1. Separating Analog and Digital Signals
SCP Pos 0 SCP Pos 1 SCP Pos 2 SCP Pos 3
SCP Pos 4SCP Pos 7 SCP Pos 6 SCP Pos 5
A
nalog Input and
Output
Digital Input and
Output
VT1534A
PWM, Freq &
Totalizer
VT1531A
Voltage DAC
VT1533A
Digital I/O
empty