C H A P T E R 2 Traditional DNS
7
Multi-Site Load Balancing
Authoritative DNS Servers
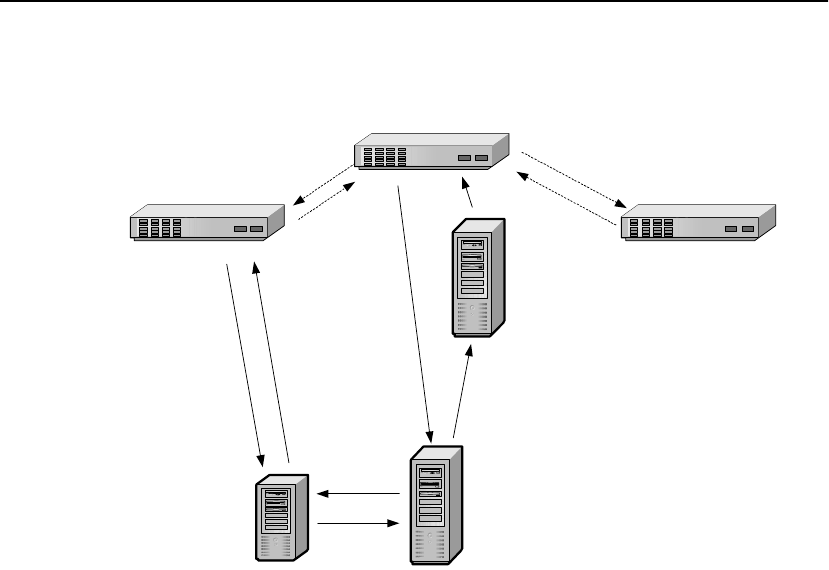
The DNS maps, or “resolves” hostnames into IP addresses. It is, in
effect, a distributed database operating through a distributed,
hierarchical system of Domain Name Servers. Thus, if the local DNS
server cannot resolve a name, it looks “upstream” to consult a Root
Domain Server for help. The Root Domain Server in turn asks the
Authoritative Name Server (i.e., the owner of the name it is trying to
resolve) to return the appropriate IP address for the requested name.
To illustrate
1. The client sends a query to its configured DNS (all clients are
configured with the address of their DNS server) to resolve a par-
ticular domain name (e.g., www.mstd-ex.com).
2. The client DNS server sends a query to the Root Domain server
for the .com domain (every DNS server is configured with the
root server information) to resolve mstd-ex.com.
3. The Root Domain server responds with the address of the
Authoritative DNS server for the mstd-ex.com domain.
7140/7170
(Los Angeles)
7190
ns.mstd-ex.com (Chicago)
Authority for msd-ex.com
Local DNS server
(San Diego)
Client
(San Diego)
7140/7170
(Chicago)