Options and Upgrades
Instruction Manual: evolution 5000 E57xx DSNG and DENG Voyager Encoder Page 3-15
ST.TM.E10076.3
3.6.4 Function of Remultiplexer
It is the function of the Remultiplexer to combine the locally generated
host services with the externally supplied input services, connected via ASI
inputs to the rear of the unit. If the Service ID (DVB) or Program Number
(ATSC), PIDs or service names, of two or more of the services clash, the
Remultiplexer can remap the Service ID or program number, remap PIDs,
and alter the service names to resolve the clash.
If a new service is detected on any input, and it clashes with an existing
service, it is the new service’s Service ID or Program Number, PIDs, or
Service Name that are remapped to resolve the conflict. Service names are
made unique by the addition of a number, for example ‘Default Service’
may be renamed ‘Default Service [2]’.
The way the Remultiplexer deals with user requests to remap PIDs
depends on its mode of operation.
When set to ‘Intelligent Mode’ (see Remux Mode Option), if the user then
attempts to move/remap a PID to a PID already being used, the
Remultiplexer allows this to happen, and automatically remaps the element
that was on that PID.
When the Remultiplexer is operating in ‘Dumb Mode’, if the user tries to
remap an element onto a PID that is already being used, it will not allow
the change to take place.
NOTE…
When operating in ‘Dumb Mode’ the Encoder may power up with unresolved PID clashes, which the
user must resolve.
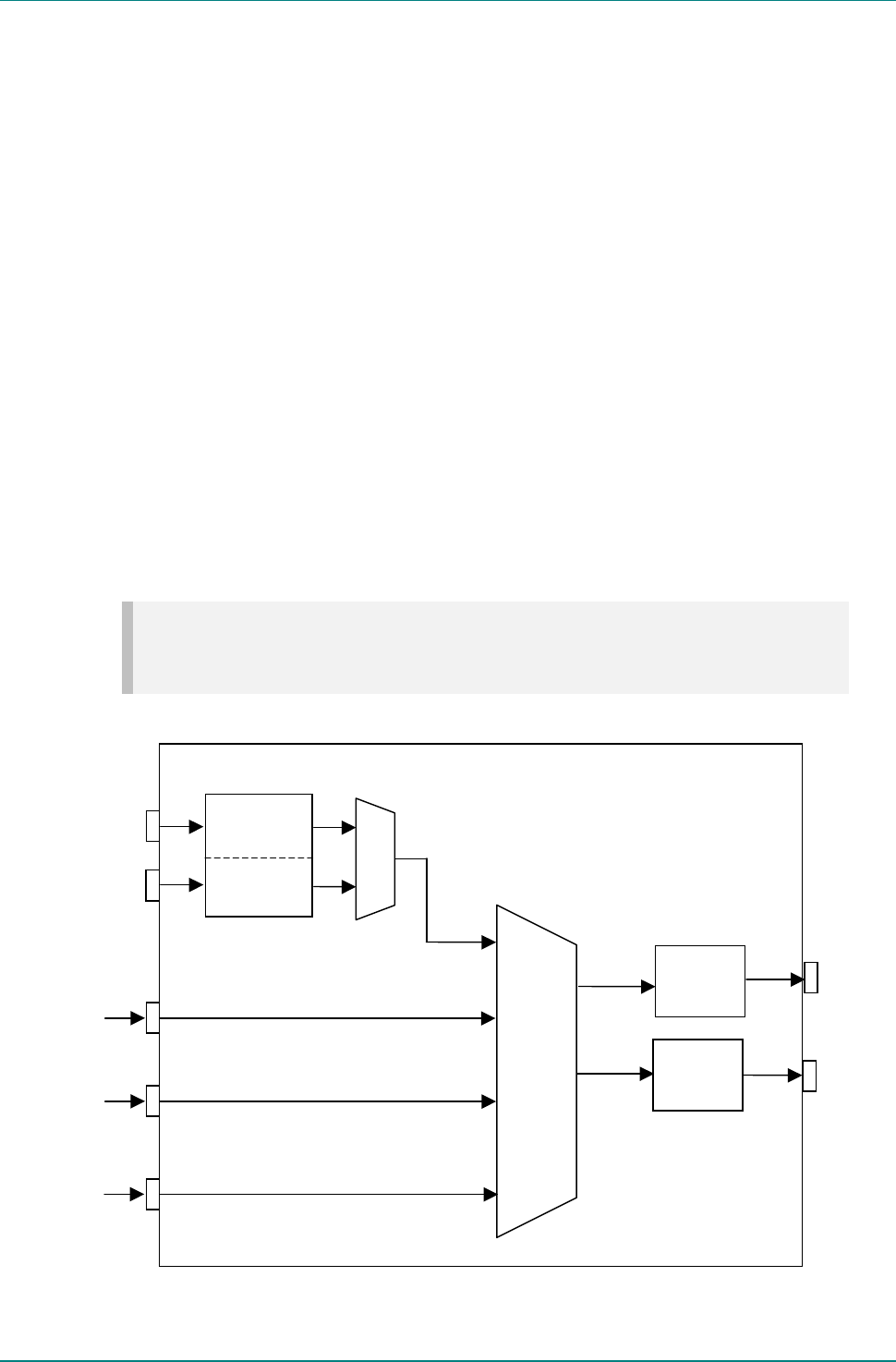
Figure 3.6: Remultiplexer Block Diagram
Dual Port
Ram
IF Out
p
ut
Remux
ASI
Input
Modulator
QPSK
Remultiplexer
Video
Video
Encoder
Audio
Encoder
A
udio
Host Mux
Host
Mux
Rate
Remux
ASI
Input
Remux
ASI
Input
Output
Bit
-
rate
ASI
Driver
ASI Output