Chapter 10 Theory of Operation • 162 USER MANUAL
Then the corresponding time constants are
T
m
= 0.04 sec
and
T
e
= 0.002 sec
Assuming that the amplifier gain is Kv = 4, the resulting transfer function is
P/V = 40/[s(0.04s+1)(0.002s+1)]
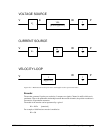
Current Drive
The current drive generates a current I, which is proportional to the input voltage, V, with a gain of Ka.
The resulting transfer function in this case is
P/V = K
a
K
t
/ Js
2
where Kt and J are as defined previously. For example, a current amplifier with K
a
= 2 A/V with the
motor described by the previous example will have the transfer function:
P/V = 1000/s
2
[rad/V]
If the motor is a DC brushless motor, it is driven by an amplifier that performs the commutation. The
combined transfer function of motor amplifier combination is the same as that of a similar brush
motor, as described by the previous equations.
Velocity Loop
The motor driver system may include a velocity loop where the motor velocity is sensed by a
tachometer and is fed back to the amplifier. Such a system is illustrated in Fig. 10.5. Note that the
transfer function between the input voltage V and the velocity ω is:
ω /V = [K
a
K
t
/Js]/[1+K
a
K
t
K
g
/Js] = 1/[K
g
(sT
1
+1)]
where the velocity time constant, T1, equals
T1 = J/K
a
K
t
K
g
This leads to the transfer function
P/V = 1/[K
g
s(sT1+1)]
Σ
K
a
Kt/Js
K
g
V
Figure 10.5 - Elements of velocity loops
The resulting functions derived above are illustrated by the block diagram of Fig. 10.6.