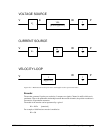
USER MANUAL Chapter 10 Theory of Operation • 165
A = 0.9
C = 1
a = 250 rad/s
and the equivalent continuous filter, G(s), is
G(s) = [16 + 0.144s + 1000/s} ∗ 250/ (s+250)
The notch filter has two complex zeros, Z and z, and two complex poles, P and p.
The effect of the notch filter is to cancel the resonance affect by placing the complex zeros on top of
the resonance poles. The notch poles, P and p, are programmable and are selected to have sufficient
damping. It is best to select the notch parameters by the frequency terms. The poles and zeros have a
frequency in Hz, selected by the command NF. The real part of the poles is set by NB and the real part
of the zeros is set by NZ.
The most simple procedure for setting the notch filter, identify the resonance frequency and set NF to
the same value. Set NB to about one half of NF and set NZ to a low value between zero and 5.
ZOH
The ZOH, or zero-order-hold, represents the effect of the sampling process, where the motor command
is updated once per sampling period. The effect of the ZOH can be modelled by the transfer function
H(s) = 1/(1+sT/2)
If the sampling period is T = 0.001, for example, H(s) becomes:
H(s) = 2000/(s+2000)
However, in most applications, H(s) may be approximated as one.
This completes the modeling of the system elements. Next, we discuss the system analysis.
System Analysis
To analyze the system, we start with a block diagram model of the system elements. The analysis
procedure is illustrated in terms of the following example.
Consider a position control system with the DMC-13X8 controller and the following parameters:
K
t
= 0.1 Nm/A Torque constant
J = 2.10
-4
kg.m
2
System moment of inertia
R = 2
Ω
Motor resistance
K
a
= 4 Amp/Volt Current amplifier gain
KP = 12.5 Digital filter gain
KD = 245 Digital filter zero
KI = 0 No integrator
N = 500 Counts/rev Encoder line density
T = 1 ms Sample period
The transfer function of the system elements are:
Motor