5 - 16
MELSEC-F
COMMUNICATION PROCEDURE5
5 - 16
5.4.1 PING command (Personal computer Ethernet module)
The following example illustrates how to confirm the completion of the initial
processing by issuing the PING command to the local station's Ethernet module from
an external device connected on the same Ethernet network. (In the example, the
confirmation is made between devices whose IP address class and sub-net address
are identical.)
<Designation method>
ping IP address
<Example>
IP address of the Ethernet module: 192.0.1.254
<When the PING command does not respond successfully>
Check the following items and send the PING command again.
• Check the Ethernet module's attachment.
• Check the connection to the Ethernet network.
• Check the contents of each parameter written to the Ethernet module.
• Check the operation condition of the Ethernet module (are there any
irregularities?).
• Check the IP address of the Ethernet module dictated by the PING command.
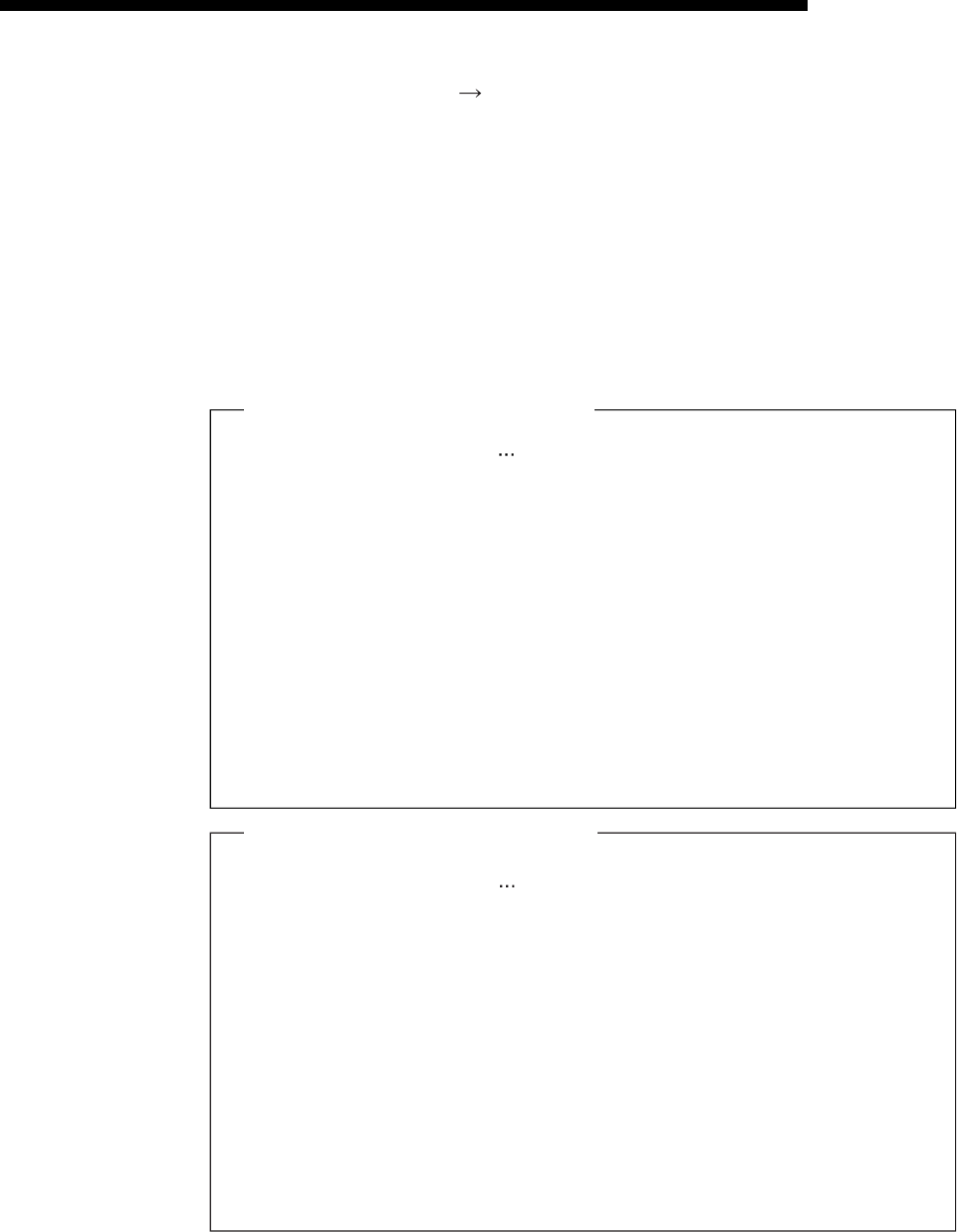
C:\>ping 192.0.1.254 Execute the ping command
Pinging 192.0.1.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.0.1.254: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.0.1.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.0.1.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.0.1.254: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.0.1.254:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss)
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms
C:\>_
Example of screen at normal completion
C:\>ping 192.0.1.254 Execute the ping command
Pinging 192.0.1.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out:
Request timed out:
Request timed out:
Request timed out:
Ping statistics for 192.0.1.254:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss)
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
C:\>_
Example of screen at abnormal completion


















