Appendices
204 UDA2182 Universal Dual Analyzer Product Manual January 2009
15.4 Appendix C - Cyanide Waste Treatment
Introduction
Uses of cyanide solutions
Cyanide solutions are used in plating baths for zinc, cadmium, copper, brass, silver and
gold. The toxic rinse waters and dumps from these operations require destruction of the
cyanide (typically to a level below 0.1 ppm) before its discharge.
Technique for cyanide destruction
The technique most often used for cyanide destruction is a one or two-stage chemical
treatment process. The first stage raises the pH and oxidizes the cyanide to less toxic
cyanate. When required, the second stage neutralizes and further oxidizes the cyanide to
harmless carbonate and nitrogen. The neutralization also allows the metals to be
precipitated and separated from the effluent.
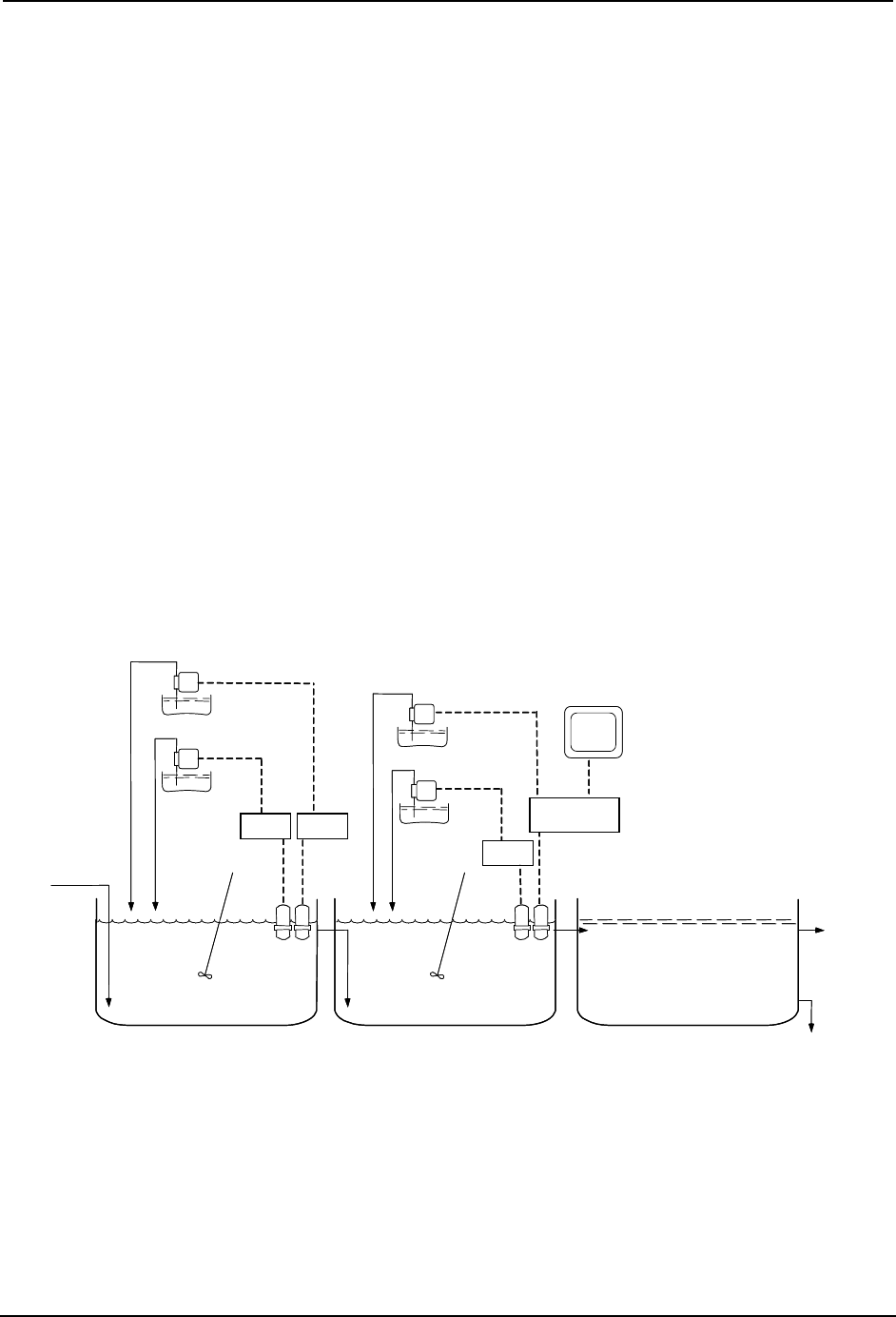
Consistent treatment and stable control in this type of process requires well-mixed
reaction tanks with enough volume for adequate retention time. See Figure 15-3.
Retention time is calculated by dividing the filled or usable tank volume by the waste
flowrate. Typically it is 10 minutes or more.
pH ANALYZER
CONTROLLER
RECORDER
PROPORTIONAL
ACID
NOTE: The separate pH and ORP
measurements and control shown
in the first stage may be handled
with a single UDA2182 Analyzer
with combined input.
ON/OFF
HYPOCHLORITE
ORP
HYPOCHLORITE
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
CAUSTIC
ORP pH
CYANIDE
WASTE
CYANIDE TO CYANATE CYANATE TO CARBONATE
AND NEUTRALIZATION
SETTLING SLUDGE
pH ANALYZER
CONTROLLER
pH ANALYZER
CONTROLLER
RECORDER
PROPORTIONAL
ACID
NOTE: The separate pH and ORP
measurements and control shown
in the first stage may be handled
with a single UDA2182 Analyzer
with combined input.
ON/OFF
HYPOCHLORITE
ORPORP
HYPOCHLORITE
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
CAUSTIC
ORPORP pH
CYANIDE
WASTE
CYANIDE TO CYANATE CYANATE TO CARBONATE
AND NEUTRALIZATION
SETTLING SLUDGE
Figure 15-3 Cyanide Treatment System


















