29
3.3 Dedicated Registers
Use the dedicated registers for specified purposes. Program counter (PC), program
status (PS), table base register (TBR), return pointer (RP), system stack pointer (SSP),
user stack pointer (USP), and multiplication/division results registers (MDH/MDL) are
prepared.
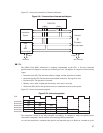
■ Dedicated Registers List
Figure 3.3-1 shows the dedicated register list.
Figure 3.3-1 Dedicated registers list
■ Program Counter (PC)
Function of program counter (PC: Program Counter) is described.
The program counter (PC) consists of 32-bit.
Figure 3.3-2 shows the bit configuration of the program counter (PC).
Figure 3.3-2 Program counter (PC)
The address of the executed instruction is shown with the program counter.
If the PC is updated when an instruction is executed, Bit 0 is set to "0". Bit 0 may be "1" only when an odd
address is specified as the branch destination address.
Even in that case, bit 0 is invalid, and the command must be placed in the address of the multiple of two.
The initial value by reset is irregular.
■ Program Status Register (PS)
This register retains the program status, and is separated into three parts, namely, ILM, SCR, and CCR.
Refer to "3.3.1 Program Status Register (PS)" for details.
The undefined bits are all reserved bits. When the register is read, "0" is always read. Writing is invalid.
Program counter (PC)
Program status (PS) ILM SCR CCR
Table base register (TBR)
Return pointer (RP)
System stack pointer (SSP)
User stack pointer (USP)
Multiplication and division result register
(MDH)
(MDL)
XXXXXXXX
H
31 0 Initial value
bit