INTERRUPT STRUCTURE S3F80JB
5-12
INTERRUPT PRIORITY REGISTER (IPR)
The interrupt priority register, IPR (FFH, Set 1, Bank 0), is used to set the relative priorities of the interrupt levels
used in the microcontroller’s interrupt structure. After a reset, all IPR bit values are undetermined and must
therefore be written to their required settings by the initialization routine.
When more than one interrupt source is active, the source with the highest priority level is serviced first. If both
sources belong to the same interrupt level, the source with the lowest vector address usually has priority (This
priority is fixed in hardware).
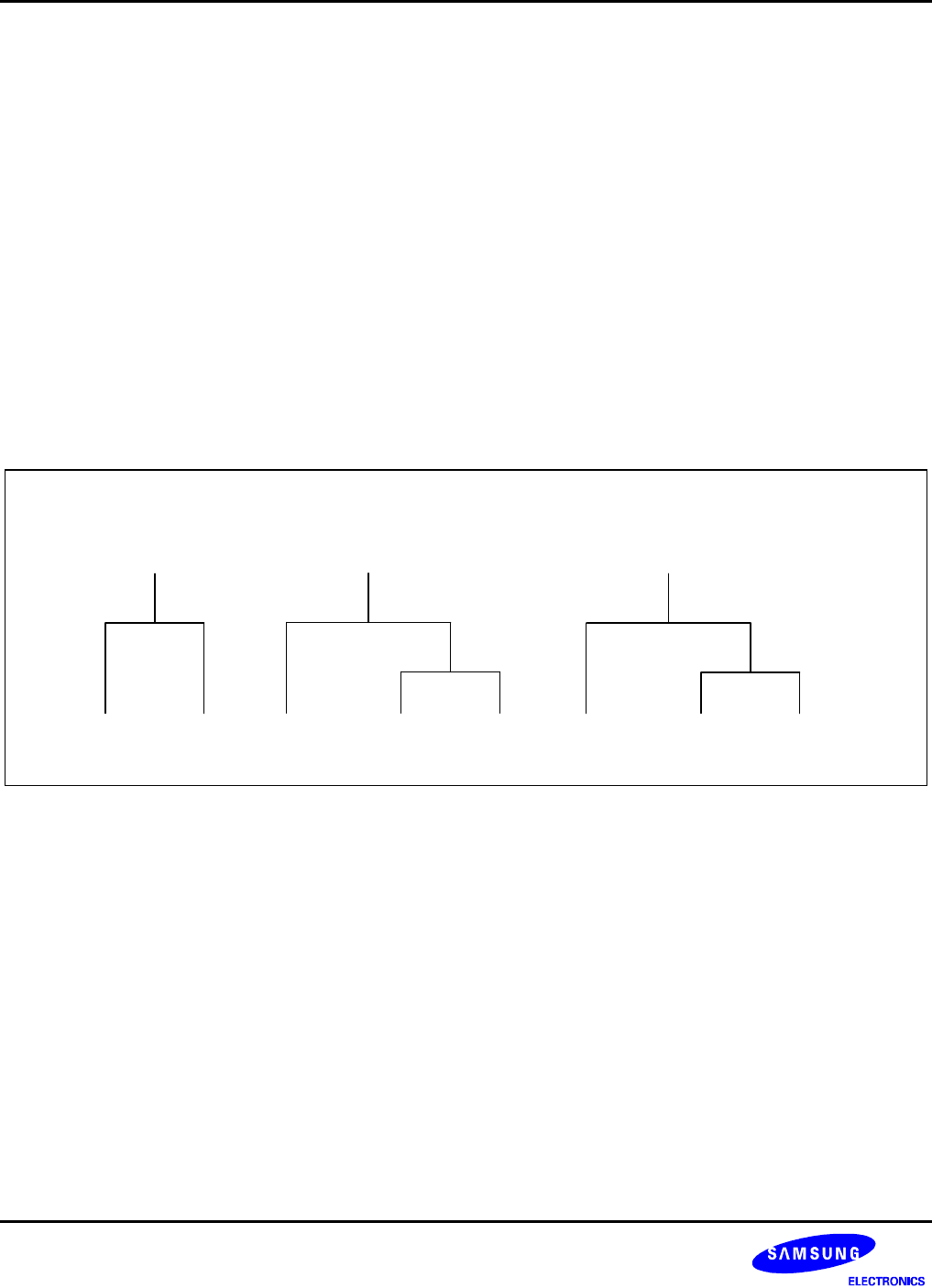
To support programming of the relative interrupt level priorities, they are organized into groups and subgroups by
the interrupt logic. Please note that these groups (and subgroups) are used only by IPR logic for the IPR register
priority definitions (see Figure 5–7):
Group A IRQ0, IRQ1
Group B IRQ2, IRQ3, IRQ4
Group C IRQ5, IRQ6, IRQ7
IPR
Group A
IRQ1
A2
IRQ0
A1
IRQ5
C1
IRQ7
IPR
Group C
IRQ6
C21
C2
C22
IRQ2
B1
IRQ4
IPR
Group B
IRQ3
B21
B2
B22
Figure 5-7. Interrupt Request Priority Groups
As you can see in Figure 5-8, IPR.7, IPR.4, and IPR.1 control the relative priority of interrupt groups A, B, and C.
For example, the setting '001B' for these bits would select the group relationship B > C > A; the setting '101B'
would select the relationship C > B > A.
The functions of the other IPR bit settings are as follows:
— IPR.5 controls the relative priorities of group C interrupts.
— Interrupt group B has a subgroup to provide an additional priority relationship between for interrupt levels 2, 3,
and 4. IPR.3 defines the possible subgroup B relationships. IPR.2 controls interrupt group B.
— IPR.0 controls the relative priority setting of IRQ0 and IRQ1 interrupts.


















