FX Series Programmable Controlers Applied Instructions 5
5-60
5.6.7 SPD (FNC 56)
Operation:
The number of pulses received at S
1
are counted
and stored in D
+1
; this is the current count value.
The countin
g
takes place over a set time frame
specified b
y
S
2
in msec. The time remainin
g
on the
current ‘timed count’, is displa
y
ed in device D
+2
.
The number of counted pulses (of S
1
) from the last
timed count are stored in D. The timin
g
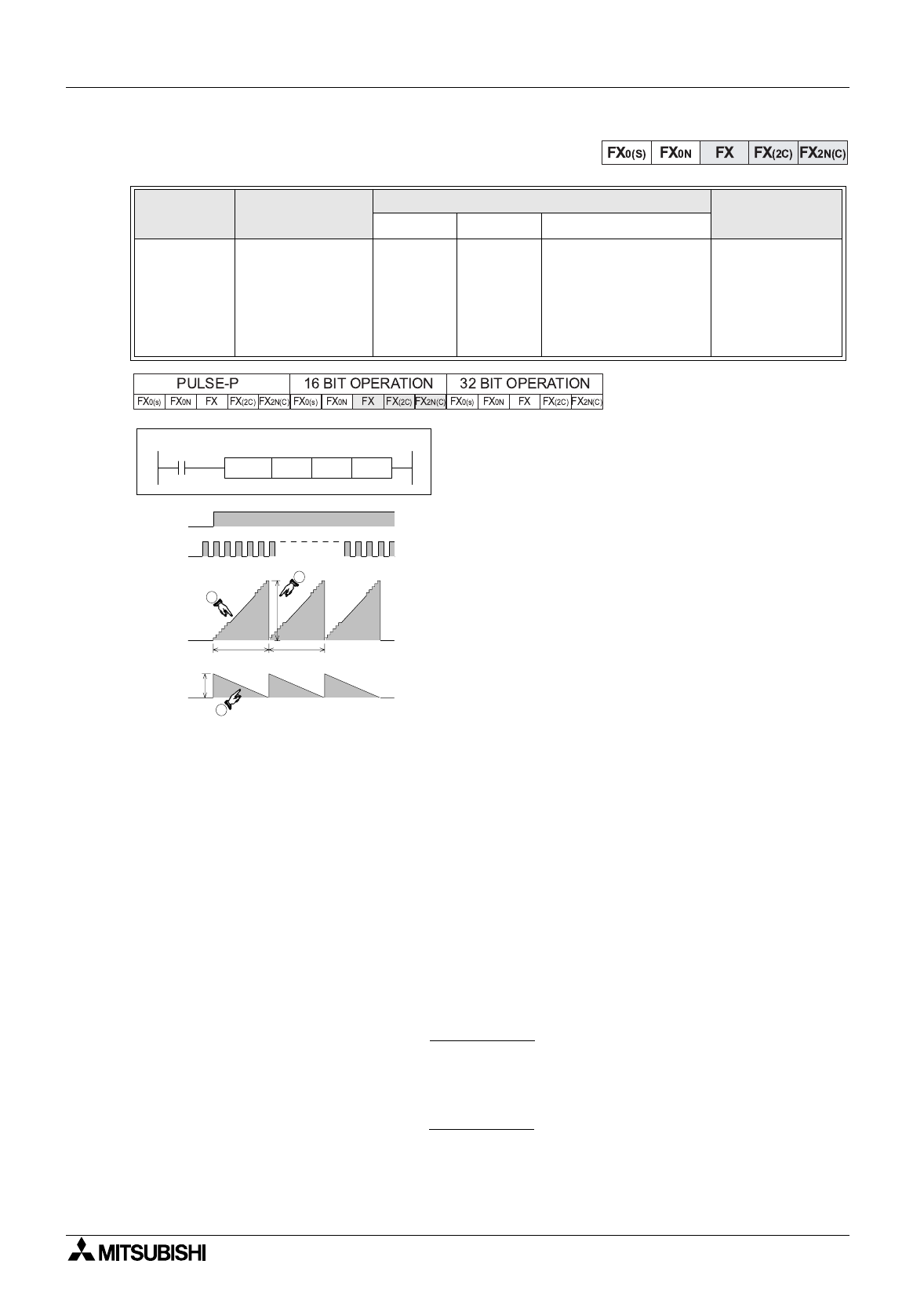
chart
opposite shows the SPD operation in a
g
raphical
sense. Note:
¿
: Current count value, device D
+1
¡
: Accumulated/ last count value, device D
¬
: Current time remainin
g
in msec, device D+2
Points to note:
a) When the timed count frame is completed the data stored in D
+1
is immediatel
y
written to D.
D
+1
is then reset and a new time frame is started.
b) Because this is both a hi
g
h speed and an interrupt process onl
y
inputs X0 to X5 ma
y
be
used as the source device S
1
. However, the specified device for S
1
must
NOT
coincide with
an
y
other hi
g
h speed function which is operatin
g
, i.e. a hi
g
h speed counter usin
g
the same
input. The SPD instruction is considered to act as a sin
g
le phase counter.
c) Multiple SPD instructions ma
y
be used, but the identified source devices S
1
restrict this to a
maximum of 6 times.
d) Once values for timed counts have been collected, appropriate speeds can be calculated
usin
g
simple mathematics. These speeds could be radial speeds in rpm, linear speeds in M/
min it is entirel
y
down to the mathematical manipulation placed on the SPD results. The
followin
g
interpretations could be used;
Mnemonic Function
Operands
Program steps
S
1
S
2
D
SPD
FNC 56
(Speed
detection)
Detects the
number of
‘encoder’ pulses
in a
g
iven time
frame. Results
can be used to
calculate speed
X0 to X5 K, H,
KnX, KnY,
KnM, KnS,
T, C, D, V,
Z
T, C, D, Z (V)
Note:
3 consecutive devices
are used. In the case
of
D= Z monitor D8028,
D8029 and D8030
SPD:
7 steps
X10
K100X 0 D 0SPD
[ S1 ]
[ S2 ]
[ D ]
2
1
3
X10
S1
S2
S2
Linear speed N (km/h) =
3600
×
(D)
n
×
S
2
×
10
3
Radial speed N (rpm) =
60
×
(D)
n
×
S
2
×
10
3
where n = the number of encoder pulses per revolution of the encoder disk.
where n = the number of linear encoder divisions per kilometer.


















