3 - 2
3.1 Performance Specifications
3
SPECIFICATIONS
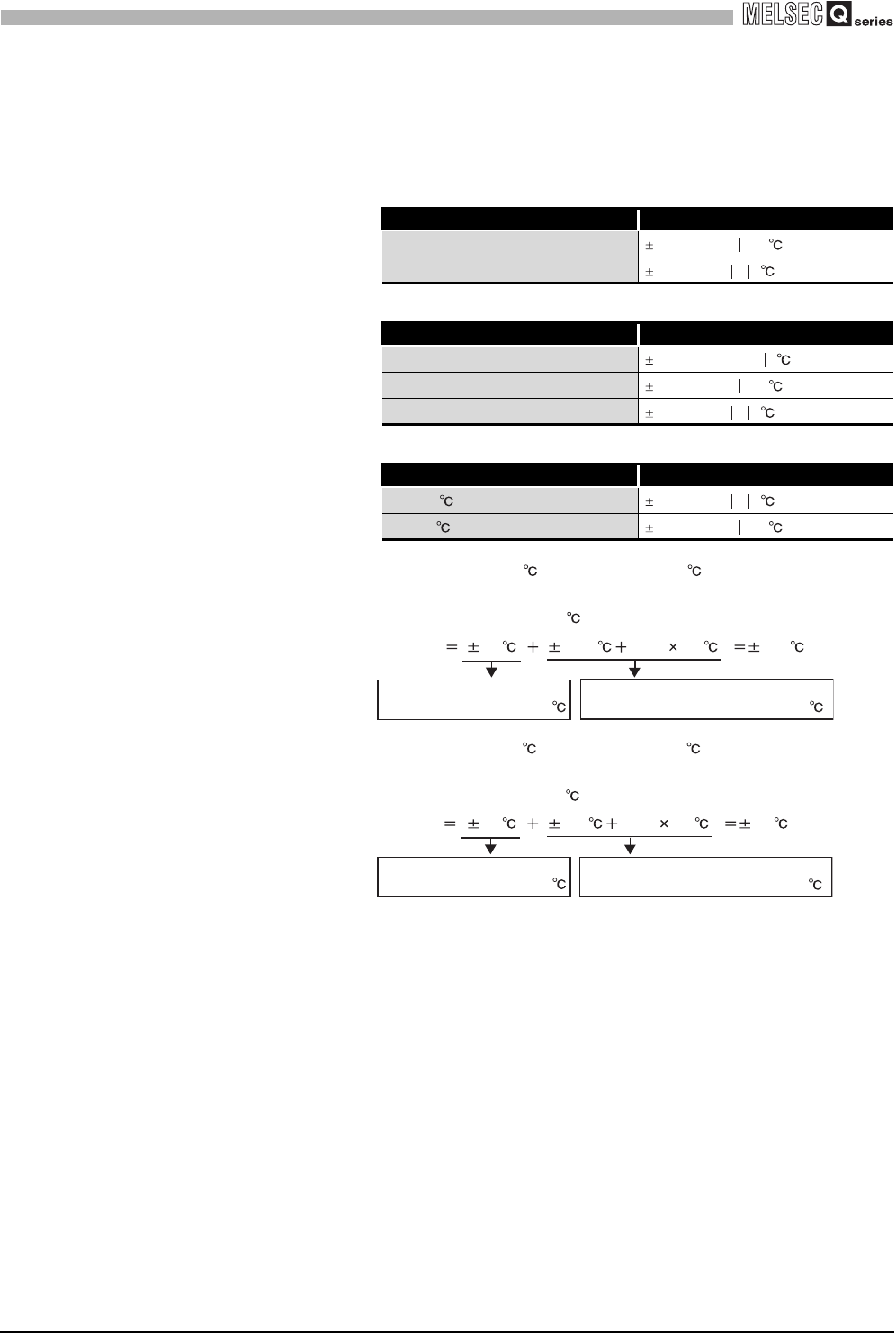
* 2 When a RTD is connected, the degree of accuracy will be the sum of the conversion accuracy of
the Q68RD3-G and the tolerance of the connected RTD.
Use the calculation formula below.
(Accuracy) = (Conversion accuracy) + (Tolerance of connected RTD)
* 3 The conversion speed indicates the time required before the measured temperature values are
stored into the buffer memory when sampling processing is specified.
Regardless of the number of conversion-enabled channels, the measured temperature values of
all channels are batch-stored into the buffer memory every 320ms. (Refer to Section 3.2.1.)
* 4 When disconnection state is detected, output values are selected from "Up scale", "Down scale" or
"Given value". (Refer to Section 3.2.2.)
* 5 Only 3-wire RTDs can be used.
2-wire RTDs and 4-wire RTDs cannot be used.
Table 3.2 Pt100 Tolerance (JIS C 1604-1997, IEC 751 1983)
Class Tolerance
A
(0.15+0.002 t )
B
(0.3+0.005 t )
Table 3.3 JPt100 Tolerance (JIS C 1604-1981)
Class Tolerance
0.15
(0.15+0.0015 t )
0.2
(0.15+0.002 t )
0.5
(0.3+0.005 t )
Table 3.4 Ni100 Tolerance (DIN 43760 1987)
Class Tolerance
0 to 250 (0.4+0.007 t )
-60 to 0 (0.4+0.0028 t )
Example 1
Ambient temperature: 40 (for Pt100 (-200 to 850 ))
RTD type: Pt100 Class A
Measurement temperature: 800
Example 2
Ambient temperature: 25 (for Pt100 (-200 to 850 ))
RTD type: Pt100 Class B
Measurement temperature: 500
(Accuracy) ( 2.4 ) { (0.15 0.002 800 )} 4.15
Conversion accuracy with
ambient temperature at 40
Tolerance of Pt100 with measured
temperature of RTD class A at 800
(Accuracy) ( 0.8 ) { (0.3 0.005 500 )} 3.6
Conversion accuracy with
ambient temperature at 25
Tolerance of Pt100 with measured
temperature of RTD class B at 500
