Programming and Operating Concepts
Video Recorder – User Manual 75
Performing Data Storage
Configuring the instrument to store the first category, Data Storage (process and diagnostic data) is done
through an Online menu entitled DATA STORAGE. All aspects of preparing a DOS formatted disk to
accept process and diagnostic data information are managed through this menu’s selections. Process
and diagnostic data may be stored on the same disk, but not along with other storage types (i.e.,
configuration, setpoint programs, or calibration).
The four types of process data are:
Trends - Data comprising the classic horizontal or vertically oriented time-varying traces that represent
process parameters.
Unit Data - Process parameter information collected and displayed in tabular or datalog format.
Alarms - A record of any alarms that activated while the instrument was monitoring and/or controlling
your process.
Events - A record of any discrete events that might have occurred while the instrument was monitoring
and/or controlling your process. Discrete events may occur, for example, in the instrument’s execution of
a set point profile.
When the instrument is On line and performing Data Storage, a separate and distinct disk file will be
established for each process data type along with a file for diagnostic errors. Each file will be
distinguished by a file extension as indicated in Table 3-11.
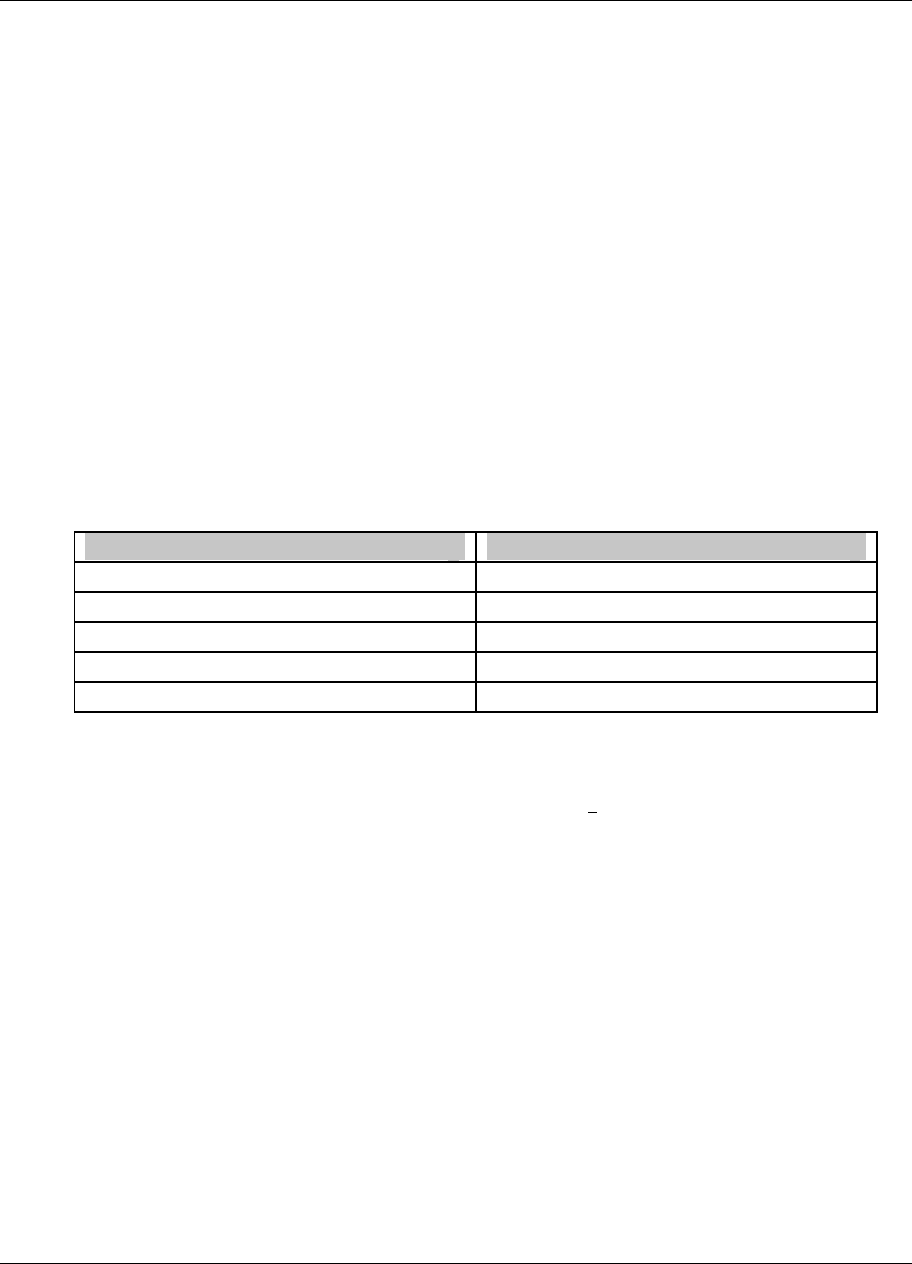
Table 3-11 Data Storage File Extensions
Data Type File extension
Trends .LNT
Unit Data .LNU
Alarm History .LNA
Discrete Event .LNE
Diagnostics .LND
You can specify which process data types are written to disk and whether or not diagnostic errors are
stored by setting up data storage schedules, accessible under a prompt entitled SET UP NEW
SCHEDULES under the DATA STORAGE menu. Up to Eight files may be written to disk while the
instrument performs Data Storage – four trend files, one unit data file, one alarm file, one event file, and
one diagnostics file.
SET UP NEW SCHEDULES lets you designate several other parameters, such as the data storage rate
(i.e., the distance in time between adjacent samples of a recorded process data parameter), the eight-
character file names used to identify each process and diagnostic data file, and whether or not the Data
Storage takes place in continuous or batch modes. Data Storage files may be configured to “rollover”
after they have become full. That is, after the space on the disk for each file type has run out, all of the
oldest data on the disk is overwritten with the most recent data.