General Operation
42 AX2500/2850 Motor Controller User’s Manual Version 1.7. February 1, 2005
Command Control Curves
The AX2500/2850 can also be set to translate the joystick or RS232 motor commands so
that the motors respond differently whether the joystick is near the center or near the
extremes.
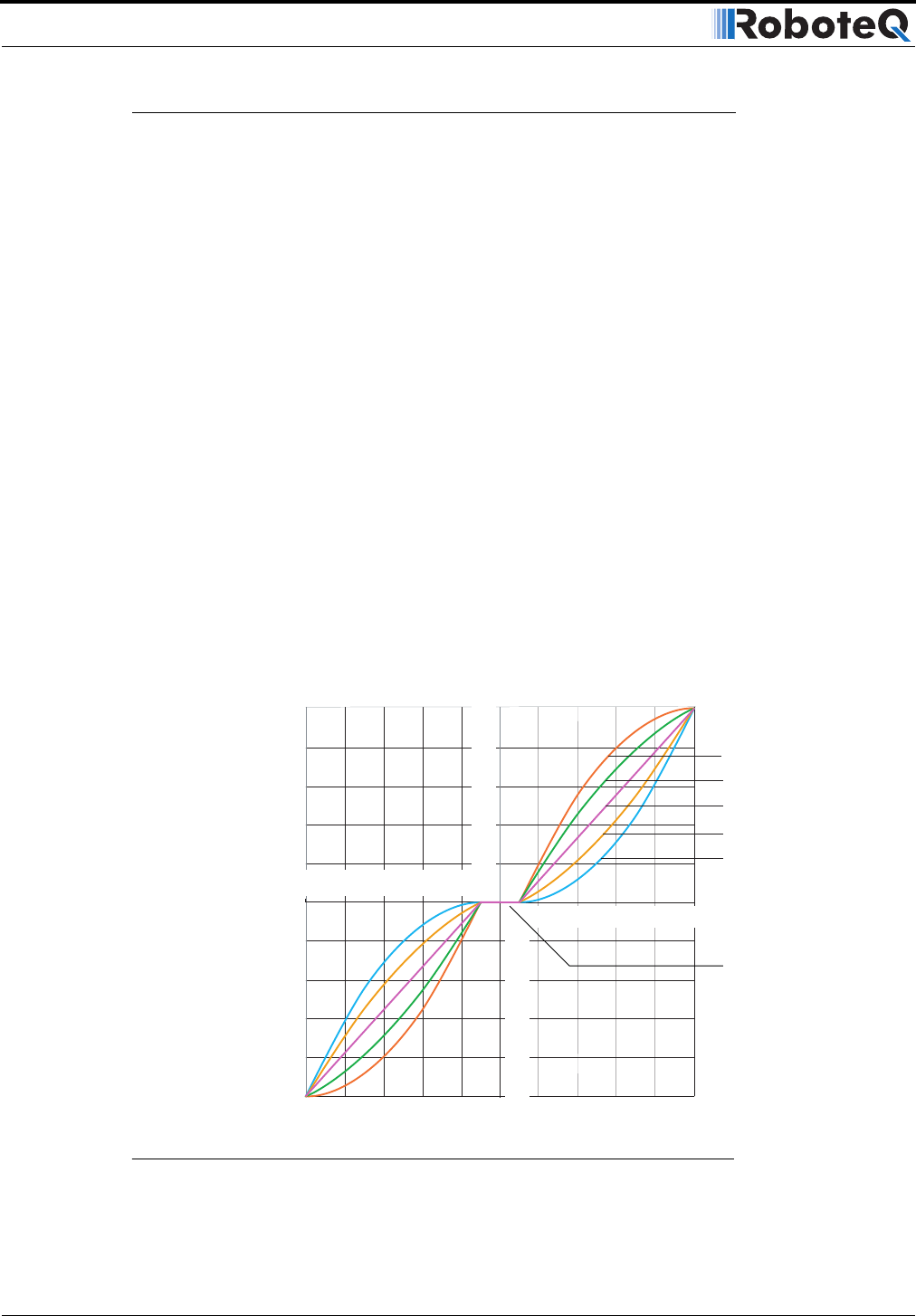
The controller can be configured to use one of 5 different curves independently set for
each channel.
The factory default curve is a “linear” straight line, meaning that after the joystick has
moved passed the deadband point, the motor’s speed will change proportionally to the joy-
stick position.
Two “exponential’ curves, a weak and a strong, are supported. Using these curves, and
after the joystick has moved past the deadband, the motor speed will first increase slowly,
increasing faster as the joystick moves near the extreme position. Exponential curves allow
better control at slow speed while maintaining the robot’s ability to run at maximum speed.
Two “logarithmic” curves, a weak and a strong, are supported. Using these curves, and
after the joystick has moved past the deadpoint, the motor speed will increase rapidly, and
then increase less rapidly as the joystick moves near the extreme position.
The graph below shows the details of these curves and their effect on the output power as
the joystick is moved from its center position to either extreme. The graph is for one joy-
stick only. The graph also shows the effect of the deadband setting.
20
40
60
80
100
0
20
40
60
80
100
- 20
- 40
- 60
- 80
- 100
20
40
60
80
100
% Forward
(Motor Output)
Logarithmic Strong
Logarithmic Weak
Linear (default)
Exponential Weak
Exponential Strong
% Reverse
% Command Input
Deadband
FIGURE 16. Exponentiation curves


















