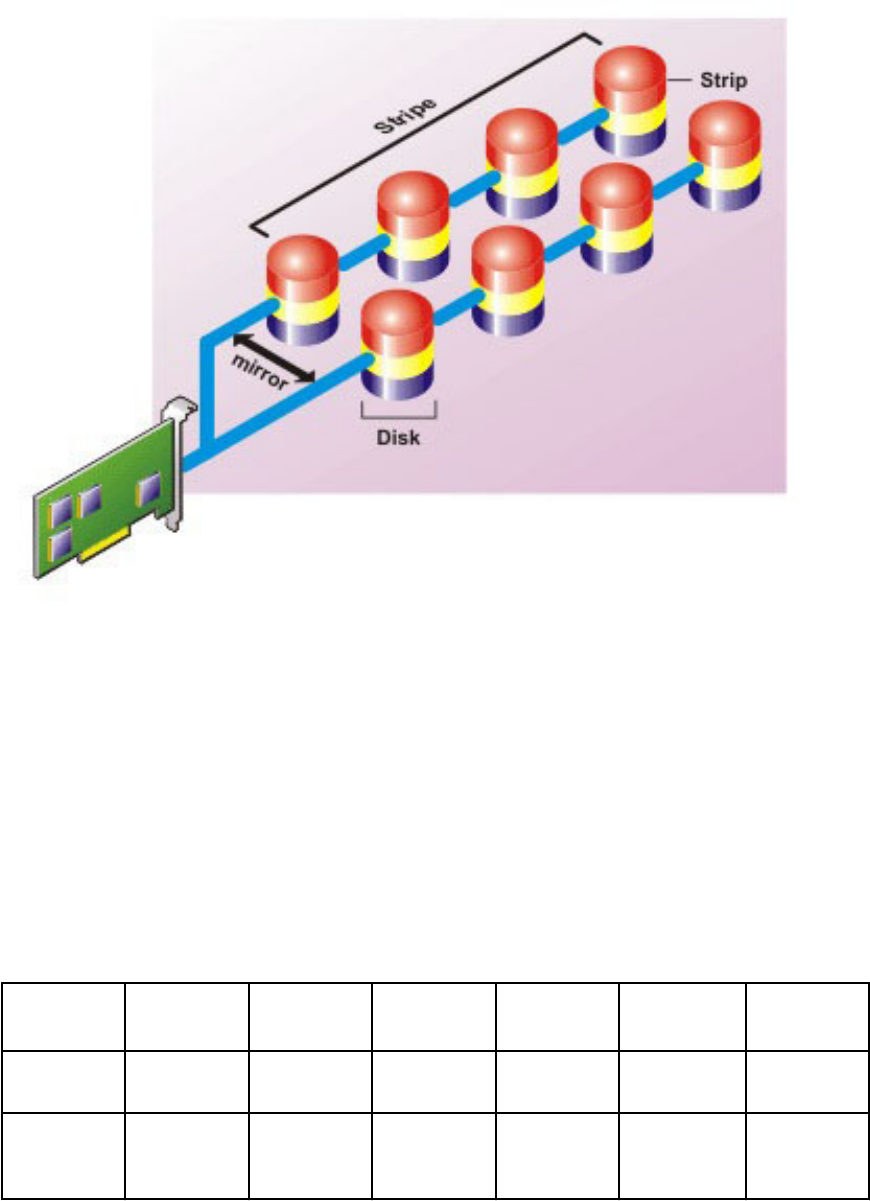
RAID 10 characteristics:
• Groups n disks as one large virtual disk with a capacity of (n/2) disks, where n is an even integer.
• Mirror images of the data are striped across sets of physical disks. This level provides redundancy
through mirroring.
• When a disk fails, the virtual disk still works. The data is read from the surviving mirrored disk.
• Improved read performance and write performance.
• Redundancy for protection of data.
Comparing RAID Level Performance
The following table compares the performance characteristics associated with the more common RAID
levels. This table provides general guidelines for choosing a RAID level. Evaluate your specific
environment requirements before choosing a RAID level.
Table 25. RAID Level Performance Comparison
RAID Level Data
Availability
Read
Performanc
e
Write
Performanc
e
Rebuild
Performanc
e
Minimum
Disks
Required
Suggested
Uses
RAID 0 None Very Good Very Good N/A N Noncritical
data.
RAID 1 Excellent Very Good Good Good 2N (N = 1) Small
databases,
database
213


















