Model 9110TH NOx Analyzer Remote Operation
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 185
8. REMOTE OPERATION
This section provides information needed when using external digital and serial I/O for remote operation.
It assumes that the electrical connections have been made as described in Section 3.3.1.
The T100 can be remotely configured, calibrated or queried for stored data through the serial ports, via
either Computer mode (using a personal computer) or Interactive mode (using a terminal emulation
program).
8.1. COMPUTER MODE
Computer Mode is used when the analyzer is connected to a computer with a dedicated interface
program such as APICOM.
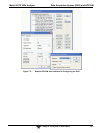
8.1.1. REMOTE CONTROL VIA APICOM
APICOM is an easy-to-use, yet powerful interface program that allows the user to access and control any
of TAI's’ main line of ambient and stack-gas instruments from a remote connection through direct cable,
modem or Ethernet. Running APICOM, a user can:
Establish a link from a remote location to the 9110T through direct cable connection via RS-232
modem or Ethernet.
View the instrument’s front panel and remotely access all functions that could be accessed manually
on the instrument.
Remotely edit system parameters and set points.
Download, view, graph and save data for predictive diagnostics or data analysis.
Retrieve, view, edit, save and upload DAS configurations (Section 7.2.1).
Check on system parameters for troubleshooting and quality control.
APICOM is very helpful for initial setup, data analysis, maintenance and troubleshooting. Refer to the
APICOM manual available for download from http://www.teledyne-api.com/software/apicom/.
8.2. INTERACTIVE MODE
Interactive mode is used with a terminal emulation programs or a “dumb” computer terminal.
8.2.1. REMOTE CONTROL VIA A TERMINAL EMULATION PROGRAM
Start a terminal emulation programs such as HyperTerminal. All configuration commands must be
created following a strict syntax or be pasted in from a text file, which was edited offline and then
uploaded through a specific transfer procedure. The commands that are used to operate the analyzer in
this mode are listed in Table 8-1 and in Appendix A.