Model 9110T NOx Analyzer EPA Protocol Calibration
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 225
To provide for documentation and accountability of activities, a checklist should be compiled and then
filled out by the field operator as each activity is completed.
For information on shelter and sample inlet system, an in-depth study is in Field Operations Guide for
Automatic Air Monitoring Equipment, Publication No. APTD-0736, PB 202-249 and PB 204-650, U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air Programs, October 1972
10.5. GAS PHASE TITRATION (GPT)
10.5.1. GPT PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
Gas phase titration (GPT) is recommended during calibration of the 9110T. Those using a NO
2
permeation tube should refer to the CFR
1
.
The principle of GPT is based on the rapid gas phase reaction between NO and O
3
that produces
stoichiometric quantities of NO
2
as shown by the following equation:
Equation 10-1
hONOONO
223
Given that the O
3
concentration is known for this reaction, the resultant concentration of NO
2
can be
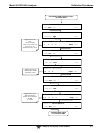
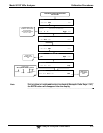
determined. Ozone is added to excess NO in a dynamic calibration system as shown in Figure 10-1,
and the NO channel of the chemiluminescence analyzer detects the changes in NO concentration.
After the addition of O
3
, the observed decrease in NO concentration on the calibrated NO channel is
equivalent to the concentration of NO
2
produced.
The amount of generated NO
2
may be varied by adding varying amounts of O
3
from a stable O
3
generator.
All zero air used in this procedure should conform to the requirements stated in Section 10.2 .
Dynamic calibration systems based on this principle are commercially available, or may be assembled by
the user. A recommended calibration system is described in the Federal Register CFR
1
.
10.5.2. GPT CALIBRATOR CHECK PROCEDURE
It has been empirically determined that the NO-O
3
reaction is complete (<1% residual O
3
) if the NO
concentration in the reaction cell (ppm) multiplied by the residence time (min.) of the reactants in the
chamber is >2.75 ppm min. The theory behind the development of this equation is in the Federal
Register
1
. The following procedures and equations should be used to determine whether an existing GPT
calibration system will meet required conditions for a specific calibration.
For calibrators that have known pre-set flow rates, use equations Equation 10-6 and Equation 10-7 below
to verify the required conditions.
If the calibrator does not meet specifications, follow the complete procedure to determine what flow
modifications must be made.
1. Select an NO standard gas that has a nominal concentration in the range of 50 to
100 ppm.
Determine the exact concentration [NO]STD by referencing against an NIST-
SRM SRM, as discussed in the Q.A. Handbook.